Figure 4.
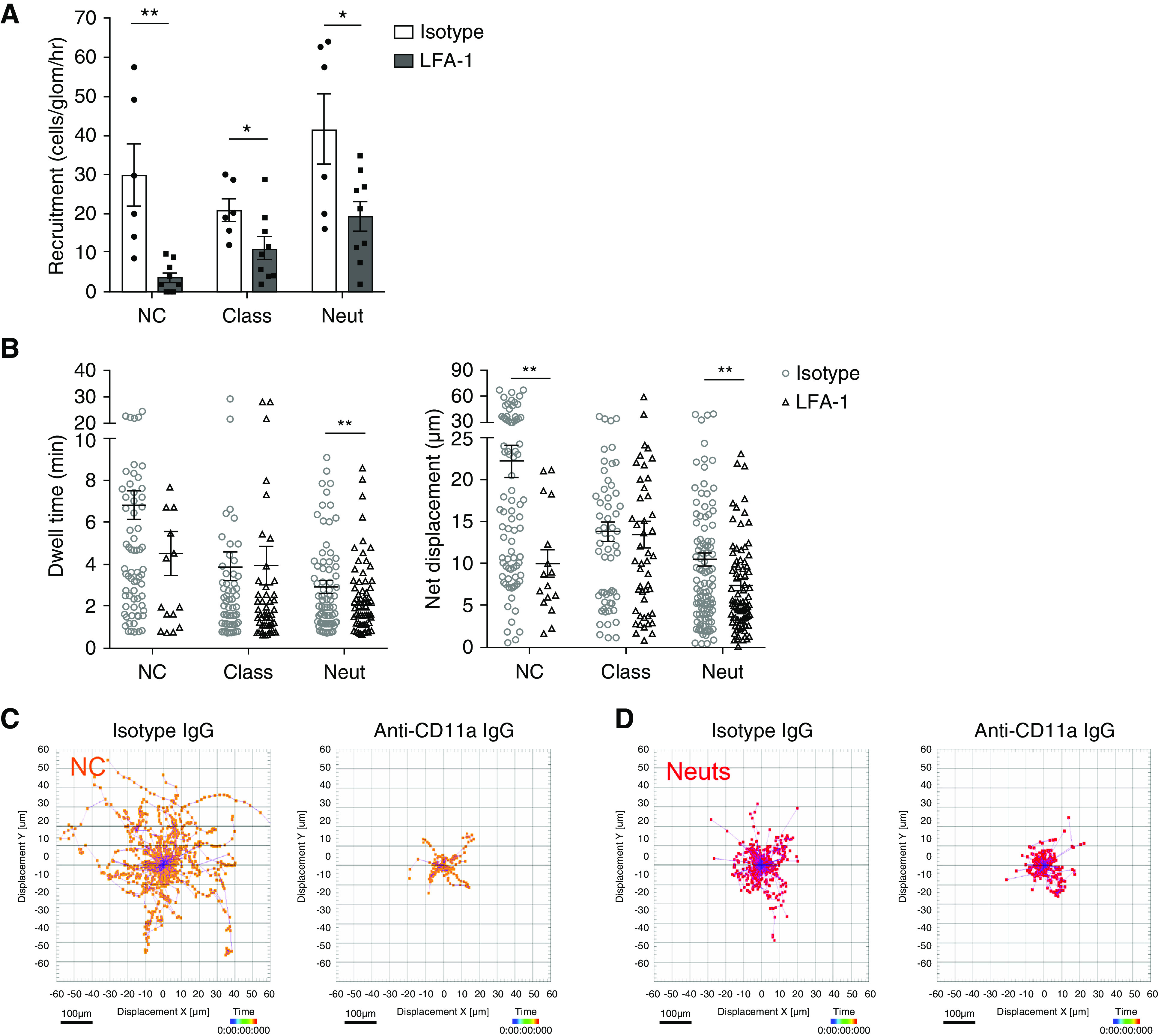
Non-classical monocyte patrolling within glomerular capillaries, and increased recruitment during NTN, is dependent on LFA-1. (A–C) Intravenous injection of 2 mg/kg of mouse anti-rat CD11a IgG was administered to WKY-hCD68-GFP rats in vivo during intravital glomerular imaging on day 2 NTN. Control WKY-hCD68-GFP rats were injected with 2 mg/kg of isotype control IgG. Leukocyte subpopulations were identified by in vivo antibody labeling with anti-rat CD43–Alexa Fluor 647 and cell behavior analyzed, as described in Figure 3. (A and B) Effect of in vivo LFA-1 inhibition on (A) glomerular recruitment and (B) dwell time and net displacement of myeloid cell populations in WKY-hCD68-GFP rats with NTN (day 2). All graphs show mean±SEM. *P<0.05; **P<0.01 versus isotype IgG, by unpaired t test. A mean of eight glomeruli from three separate experiments were analyzed for each group. Each glomerulus was imaged for 30 minutes. (C and D) Track plots for (C) GFPposCD43pos non-classical monocytes and (D) GFPnegCD43pos neutrophils in WKY-hCD68-GFP rats treated with 2 mg/kg of mouse anti-rat CD11a IgG versus isotype control IgG on day 2 NTN. All leukocyte tracks illustrated, after aligning their starting positions at the center of the plots. Displacement X (μm) versus displacement Y (μm) plotted. Scale bar, 100 µm. NC, non-classical monocytes; Class, classical monocytes; Neut, neutrophils.
