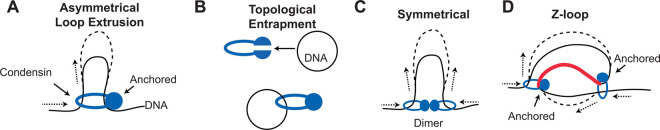
Figure 2. SMC loop extrusion.
(A) Asymmetric loop extrusion, where a loop of DNA passes through a condensin ring anchored to DNA on one side. (B) Topological loading of SMC complexes, such as cohesin, is achieved by opening of the SMC-Kleisin ring to allow DNA to enter. (C) Symmetrical loop extrusion by a dimer of condensin complexes. For this to be achieved, one condensin complex extrudes DNA on each side, with neither condensin complex anchored to the DNA. (D) A condensin Z-loop, formed when two condensin complexes pass each other on DNA. The region of DNA in red has been compacted by both condensin complexes, hence the total amount of DNA compacted by a Z-loop is less than if two condensin complexes formed two separate loops.