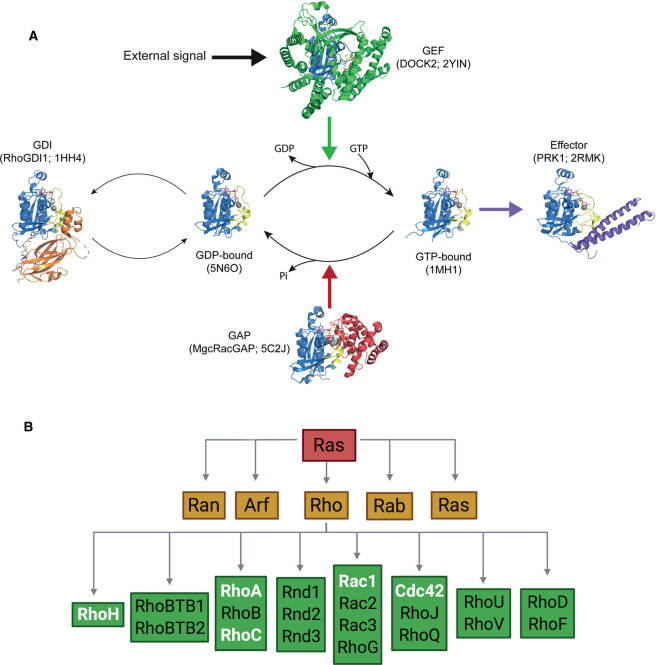
Figure 1. Introduction to the Rho-family of GTPases.
(A) The GTPase cycle of Rho-family small G proteins. Rac1 is activated when an external signal leads to GEF proteins such as DOCK2 binding, leading to stabilisation of the nucleotide-free state. The subsequent binding of GTP allows effectors to bind to the Rac1 protein. Binding of GAP proteins such as MgcRacGAP, stimulate the intrinsic GTPase activity to regenerate the GDP-bound form. RhoGDI binds to Rac1·GDP and, by sequestering the C-terminal geranylgeranyl group, removes the G protein from membranes. In each cartoon, the GTPase is shown in blue, with the switch 1 and switch 2 regions coloured yellow, the nucleotide shown as sticks and the Mg2+ ion as a grey sphere. The PDB codes of all structures are shown; the MgcRacGAP is in complex with Cdc42, all other structures are of Rac1. (B) The Ras superfamily of small GTPases separates into five families: Ran, Arf, Rho, Rab and Ras. The Rho-family further divides into several subfamilies. Family members that are the subject of discussion in this review are highlighted in white.