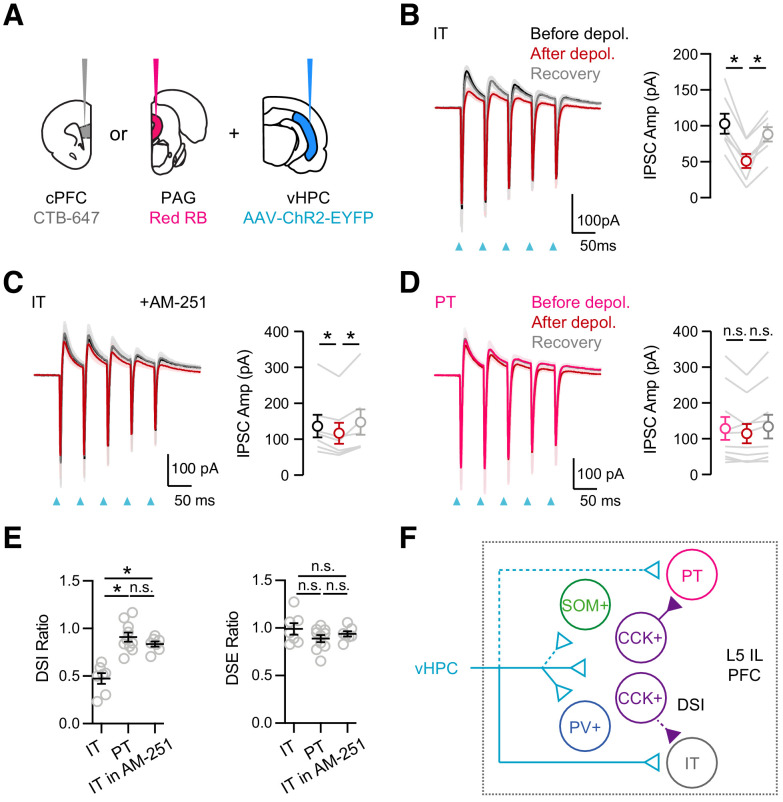
Figure 7. vHPC-evoked feed-forward inhibition at IT cells undergoes DSI.
(A) Injection schematic, showing CTB-647 in cPFC, red retrobeads (RB) in PAG, along with AAV-ChR2-EYFP in vHPC. (B) Left, Average vHPC-evoked EPSCs and IPSCs at IT cells in L5 IL PFC, before (black), immediately after depolarization (red), and after recovery (gray) (same paradigm as Figure 5). Blue arrows = light stimulation. Right, Summary of amplitudes of first vHPC-evoked IPSCs (n = 7 cells, 4 animals). (C) Similar to (B) in the presence of 10 µM AM-251, which reduces DSI (n = 7 cells, 3 animals). (D) Similar to (B) for PT cells, showing no DSI (n = 10 cells, 4 animals). (E) Summary of DSI and DSE ratios (amplitude ratios of IPSCs or EPSCs after/before the depolarizations) across the different experiments. (F) Summary schematic for vHPC-evoked feed-forward inhibition in IL PFC. vHPC inputs directly contact IT over PT cells to evoke EPSCs. vHPC inputs also engage multiple interneurons to evoke local inhibition. Inhibition mediated by CCK+ interneurons displays robust endocannabinoid-mediated DSI, but only at IT cells, and not neighboring PT cells. *p<0.05.