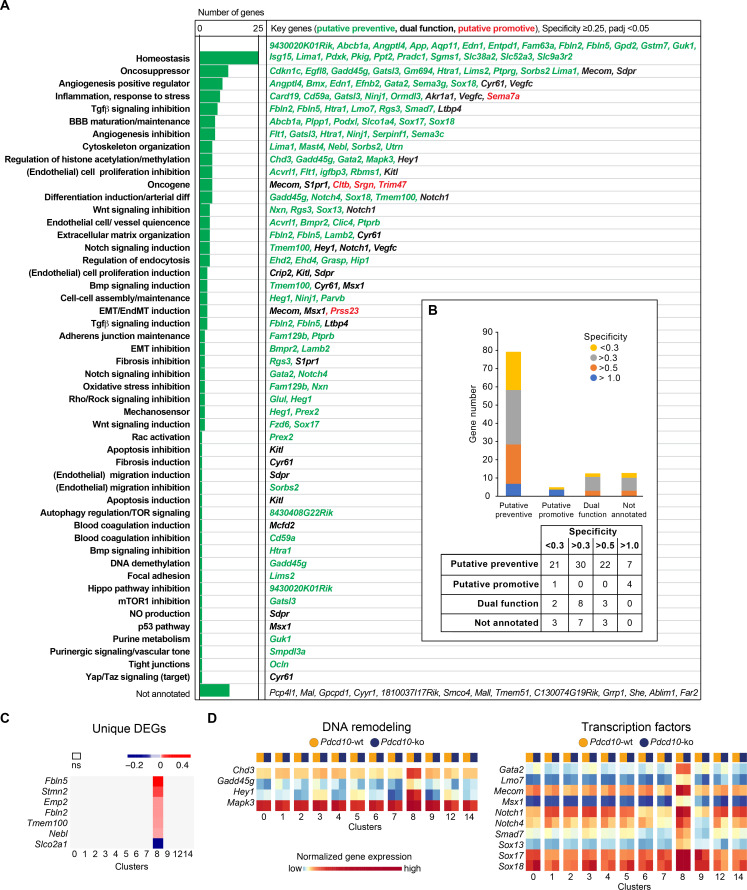
Figure 3. Unique functional markers suggest arterial Pdcd10-ko ECs may be protected from forming cavernomas.
(A) Annotation of C8 unique marker genes. 111 unique marker genes were identified using a log fold change (specificity) cutoff of 0.25 and padj <0.05. Mouse Genome Informatics (http://www.informatics.jax.org/) and PubMed (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/) were used for manual annotation (keywords: ‘gene name AND entothelial cells’ or ‘gene name’ if the previous search gave zero results). Based on the functions of these genes and the deregulation of these functions reported in Pdcd10-ko lesions, we tentatively categorized these unique marker genes into ‘preventive’ (green), ‘promotive’ (red) and ‘dual-function’ (black) (See details of annotation in Supplementary file 5 and 6). Here, 13 unique marker genes either lack clearly defined functionality or have non-EC related functions and could not be annotated. (B) Statistics of annotated unique marker genes in C8. Each gene was counted only once, although it can appear in more than one category in (A). (C) Heatmap of log fold changes of uniquely differentially expressed genes (unique DEGs) in C8. Unique DEGs were identified using thresholds: average |logFC| > 0.2 and padj <0.05. (D) Heatmap of normalized expression levels of the selected C8 unique marker genes (left: regulators of DNA remodeling; right: transcription factors) in the Pdcd10-wt and Pdcd10-ko cells in each cluster.