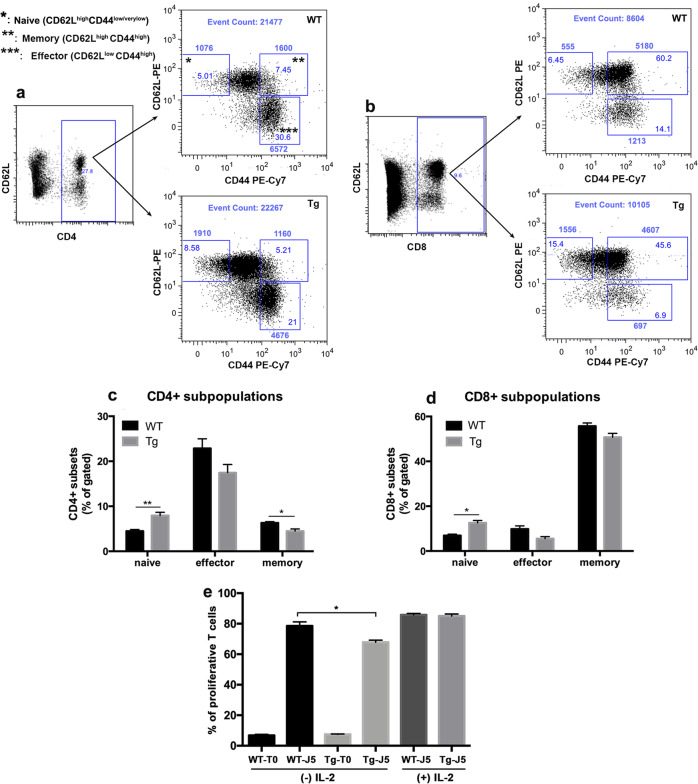
Fig. 3.
Transgenic mice develop an altered T cell phenotype. a, b Representative flow cytometry analysis of naïve, effector and memory T cells in transgenic and WT T cells. Splenocytes from 12-week-old transgenic mice (Tg) and WT mice were gated for CD4 + cells (a) or CD8 + cells (b) and analyzed for CD44 and CD62L expression. T cell subpopulations were defined as naïve (CD44low/verylowCD62Lhigh), memory (CD44highCD62Lhigh), or effector T cells (CD44highCD62Llow). The numbers inside and outside each small square indicate the percentage and the absolute number of cells, respectively. The total number of events is shown at the top. c and d Frequencies of naïve, effector and memory T cells. The results are representative of three independent experiments (n = 5 each for WT and transgenic mice). The frequency of naïve T cells in both CD4 + and CD8 + compartments was significantly increased, whereas the level of memory CD4 + T cells was decreased in transgenic mice compared to WT mice (Tg vs. WT, mean with SEM: naïve CD4 + , **p = 0.0079; naïve CD8 + , p = 0.0159; memory CD4 + , p = 0.0303, Mann-Whitney test). Although effector CD4+ and CD8 + subsets were decreased in Tg mice, this difference did not reach statistical significance. e Transgenic T cells exhibited a decreased proliferative capacity compared to WT T cells. T cells were isolated from Tg and WT mice and labeled with CFSE (1 μM). After synchronization, the cells were stimulated with anti-CD3/CD28 antibodies (1 μg/ml each). After 5 days, proliferation was analyzed by flow cytometry as the percentage of dividing cells. The addition of mouse recombinant IL2 (30 U/ml) at 24 and 72 h after stimulation restored the T cell proliferation rate, which was comparable between Tg and WT mice. Data are presented as the mean of four independent experiments. (Tg vs. WT at day 5, mean with SD: * p = 0.0286, Mann-Whitney test)