Fig. 1.
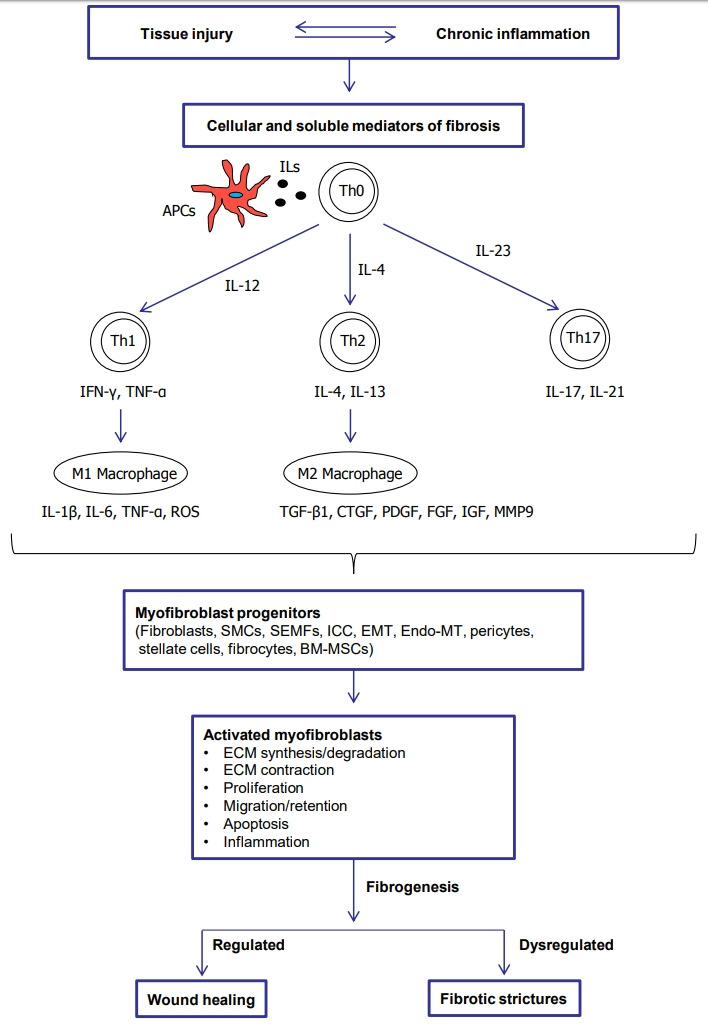
Pathophysiological process to fibrotic strictures. APCs, antigen presenting cells; ILs, interleukins; Th0, naïve T cells; Th, T helper cells; IFN-γ, interferon-γ; TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor α; ROS, reactive oxygen species; TGF-β1, transforming growth factor-β1; CTGF, connective tissue growth factor; PDGF, platelet-derived growth factor; FGF, fibroblast growth factor; IGF, insulin-like growth factor; MMP9, matrix metalloproteinase 9; SMCs, smooth muscle cells; SEMFs, subepithelial myofibroblasts; ICC, interstitial cells of Cajal; EMT, epithelial mesenchymal transition; Endo-MT, endothelial mesenchymal transition; BM-MSCs, bone marrow derived mesenchymal stem cells; ECM, extracellular matrix.
