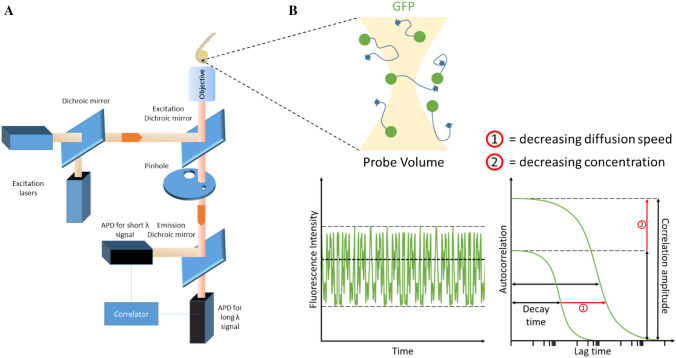
Fig. 1.
Overview of FCS set-up and zebrafish measurements. a A schematic of a typical FCS set-up. Single or dual excitation lasers can be configured to excite one or two types of fluorophores for FCS and fluorescence cross-correlation spectroscopy (FCCS), respectively. Dichroic mirrors are in place to split and/or reflect beam paths of certain wavelengths. The excitation beam is sent through the objective to excite fluorophores in a zebrafish embryo. Emission is detected back along the same optical path and through the excitation dichroic mirror. Long- and short-wavelength emissions are split by an emission dichroic mirror to allow avalanche photodiodes (APDs) to detect specific fluorophores. b Cartoon of probe volume that FCS laser beam passes through. The probe volume excites diffusing green fluorescent protein (GFP) and receives an emission spectrum. Emission beam signal intensity is recorded over time and transformed via a suitable fitting model into interpretable data that details the sample’s diffusion coefficient and concentration. (1) Reduced diffusion speed, (2) reduced concentration