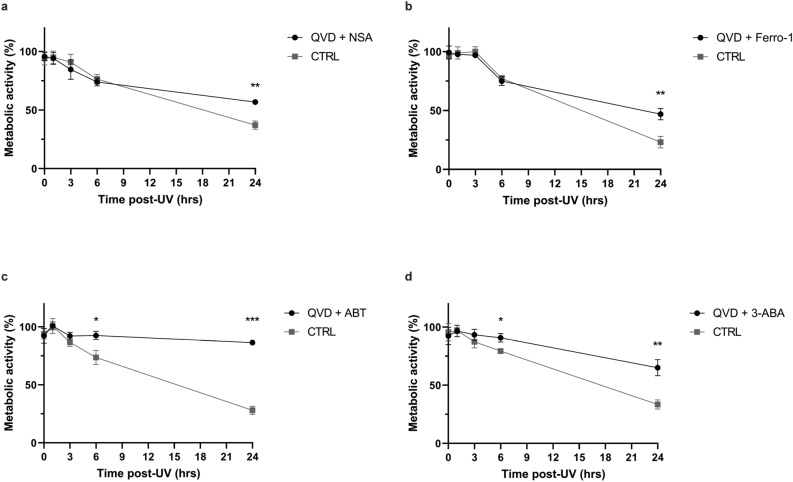
Figure 3.
UVB induces two independent reduction of cellular metabolic activity in primary human fibroblasts. Prior to UVB irradiation, fibroblasts were incubated 30 min with different combinations of cell death inhibitors. Cells were then irradiated in PBS using a lethal UVB dose (30 kJ/m2). The combinations used were: (a) Necroptosis inhibitor Necrosulfonamide (NSA, 2 μM) and caspase inhibitor Q-VD-OPh (QVD, 20 μM), (b) ferroptosis inhibitor Ferrostatin-1 (Ferro-1, 5 μM) and caspase inhibitor Q-VD-OPh (QVD, 20 μM), (c) PARP inhibitor ABT888 (ABT, 20 μM) and caspase inhibitor Q-VD-OPh (QVD, 20 μM), (d) PARP inhibitor 3-Aminobenzamide (3-ABA, 0.5 mM) and caspase inhibitor Q-VD-OPh (QVD, 20 μM). Cellular metabolic activity was assessed at different time points post UVB irradiation (0, 1, 3, 6, 24 h) using MTS assay. Irradiated cells were normalised on unirradiated cells of the same condition. NSA and Ferro-1 had no effect on cellular metabolic activity loss prevention caused by QVD. However, an additive effect of QVD and PARP inhibitors (ABT and 3-ABA) on prevention of cellular metabolic activity loss caused by UVB could be described. N = 4. *p-value < 0.05, **p-value < 0.01, ***p-value < 0.001.