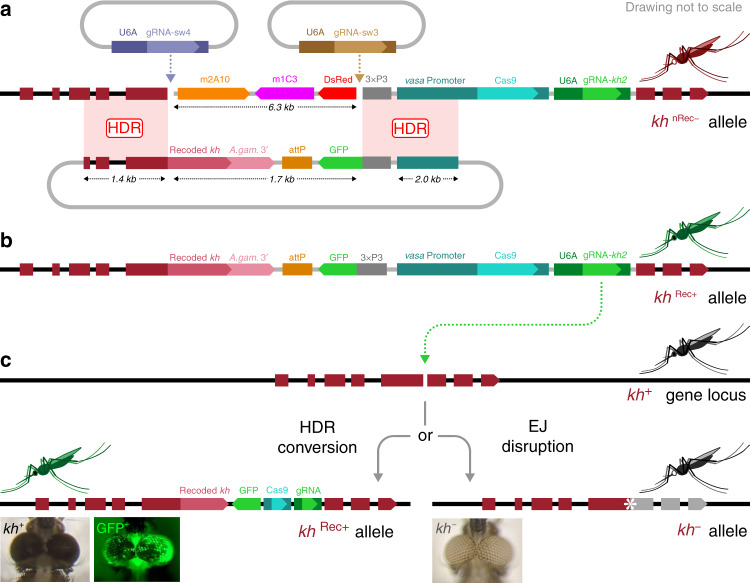
Fig. 1. The Reckh gene drive.
a Swap strategy for Cas9/gRNA-mediated cassette exchange. Two plasmid-encoded gRNAs (top) guide cleavage in the genome of the white-eyed nRec mosquito line (khnRec–)8 (middle), leading to the excision of a fragment including the DsRed eye (3xP3) marker and the two antimalarial effectors m2A10 and m1C311. The HDR template plasmid (bottom) carries homology arms flanking either cut site, promoting the insertion of a GFP-marked donor template that carries a recoded portion of the kh gene followed by the 3′-end sequence of the An. gambiae kh gene including the 3′UTR (A.gam.3′) to minimize homology. b The insertion of this unit restores kh gene function while creating a sequence (khRec+) that is uncleavable by the endogenous drive components. c The Reckh gene-drive includes an An. stephensi codon-optimized Cas9 driven by the germline-specific vasa promoter from An. stephensi and a gRNA (gRNA-kh2) directed to the fifth exon of the unmodified kh+ gene (top) regulated by the ubiquitous promoter of the An. stephensi U6A gene8. The cut in the kh gene of the Reckh mosquito germline can be repaired by drive integration via HDR (homology-directed repair) or by the less desirable EJ (end-joining) pathway (bottom). HDR results in the integration of the drive cassette that maintains kh gene function at the integration site (khRec+), while EJ usually causes the formation of loss-of-function alleles (kh−). When function is lost in both copies of the gene, individuals with white eyes are produced. kh, kynurenine hydroxylase gene; attP, φC31 recombination site; U6A, RNA polymerase-III promoter; gRNA, guide RNAs; Cas9, Cas9 open reading frame; vasa, vasa promoter; 3xP3, eye-marker promoter; GFP, green fluorescent protein; dominant marker gene. The horizontal dimension of the mosquito heads at the eyes in the images is ~1 mm.