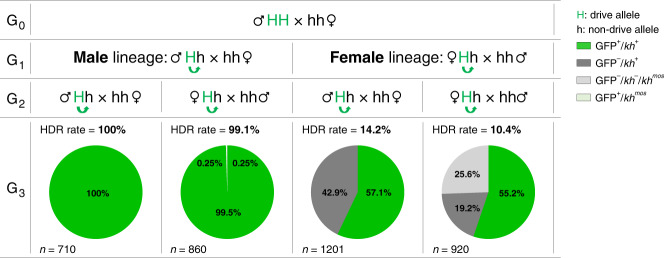
Fig. 2. Inheritance of Reckh through paternal and maternal lineages.
Charts represent the proportion of individuals inheriting the Reckh drive element (GFP+, in green) from heterozygous parents originating from drive males or drive females. The proportions of individuals that have not inherited the drive (GFP−) element and have WT black eyes (kh+) (dark grey) and those with white (kh−) or mosaic (khmos) eyes (light grey) are also shown. Rare (n = 2) drive individuals with mosaic eyes (GFP+/khmos) are depicted in light green. “H” and “h” refer to the mosquito genome at the kh locus, where “H” is the Reckh drive allele and “h” is a non-drive allele. The green arrows show the potential for conversion of the h allele in the germline. The corresponding HDR rate, i.e., the proportion of h alleles converted to H alleles is reported. Each cross was performed en masse (30 females and 15 males) in triplicate cages using drive individuals mated to WT and by screening a representative subset of individuals (n) generated in the progeny. The numbers reported are pooled from the three replicate cages. Raw data for these crosses are reported in Supplementary Table 2. Data on transmission and HDR rates reported in the “Results” section refer to the averages of progeny from both mothers and fathers originating from a male or a female drive individual.