Fig. 2. TFEB mediates the release of truncated mutant tau in primary neurons.
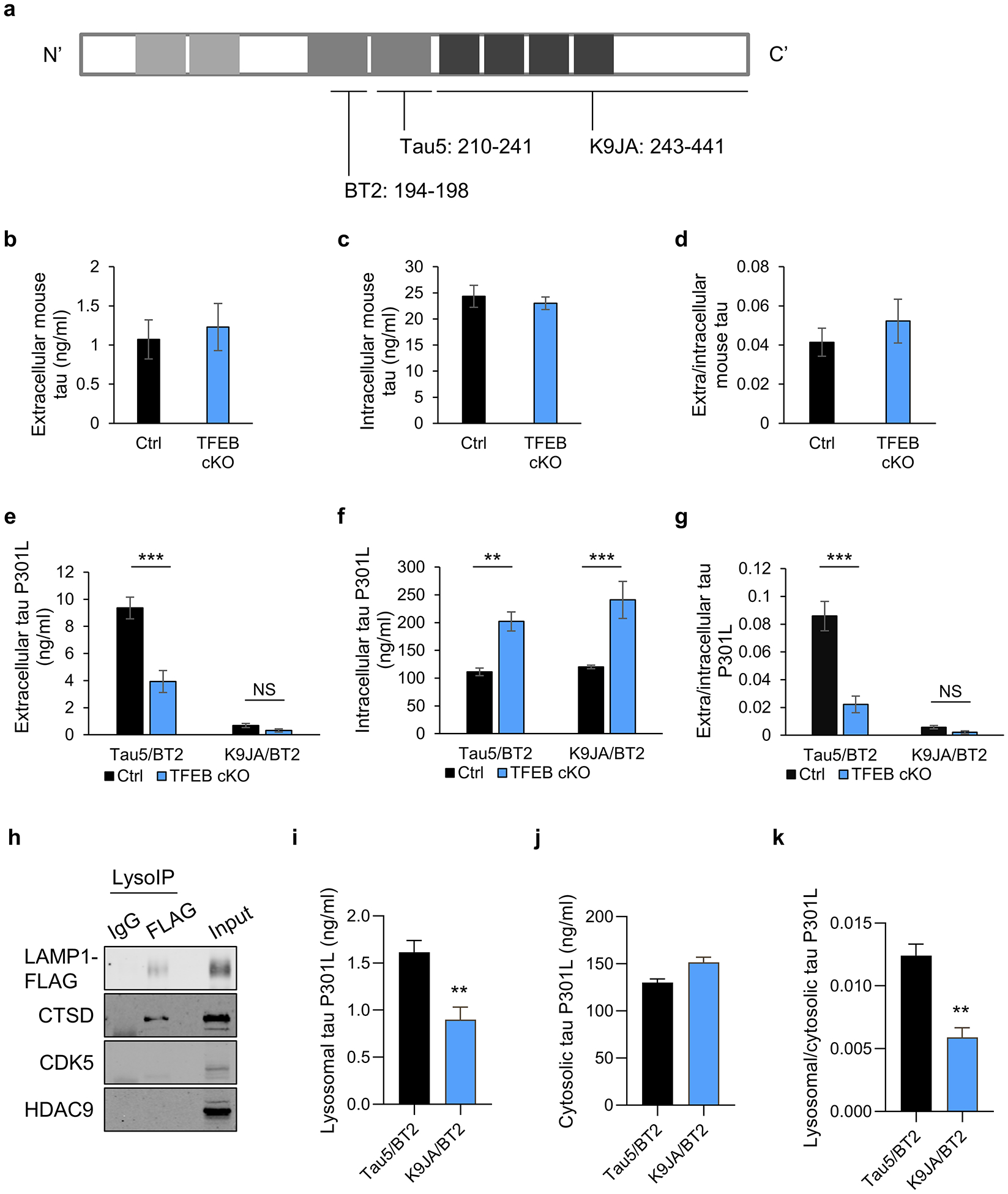
(a) Schematic of tau protein and epitopes of tau antibodies used for ELISA: Tau5 (aa 210–241), K9JA (aa 243–441), and BT2 (aa 194–198). (b-d) Extracellular (b) and intracellular (c) tau levels from cultured media or cell lysates, respectively, of WT and TFEB cKO neurons at 18 days in vitro (DIV) and quantified by ELISA (Tau5/BT2 combination). (d) Extra/intracellular tau ratio. Two tailed Student’s t-test. (n=6 of 2 experiments). (e-g) Extracellular (e) and intracellular (f) tau levels from cultured media or cell lysates of AAV-tau-P301L infected WT and TFEB cKO neurons at 18 days in vitro (DIV) and quantified by ELISA (Tau5/BT2 or K9JA/BT2 combination). (g) Extra/intracellular tau ratio. Two ways ANOVA followed by Sidak’s multiple comparisons test. (n=6 of 2 experiments). (h) Biochemical characterization of lysosomes isolated by anti-FLAG immunoprecipitation (LysoIP) using antibodies against: lysosomal membrane LAMP1, lysosomal lumen CTSD and non-lysosomal cytosolic protein CDK5 and nuclear protein HDAC9. (i-k) Lysosomal (i) and cytosolic (j) tau levels from AAV-tau-P301L infected WT and TFEB cKO neurons at 18 days in vitro (DIV) and quantified by ELISA (Tau5/BT2 or K9JA/BT2 combination). (k) Lysosomal/cytosolic tau ratio. Two tailed Student’s t-test. (n=4 of 2 experiments). Data are presented as mean ± SEM. NS, not significant; **P ≤ 0.01; ***P ≤ 0.001.
