Fig. 2.
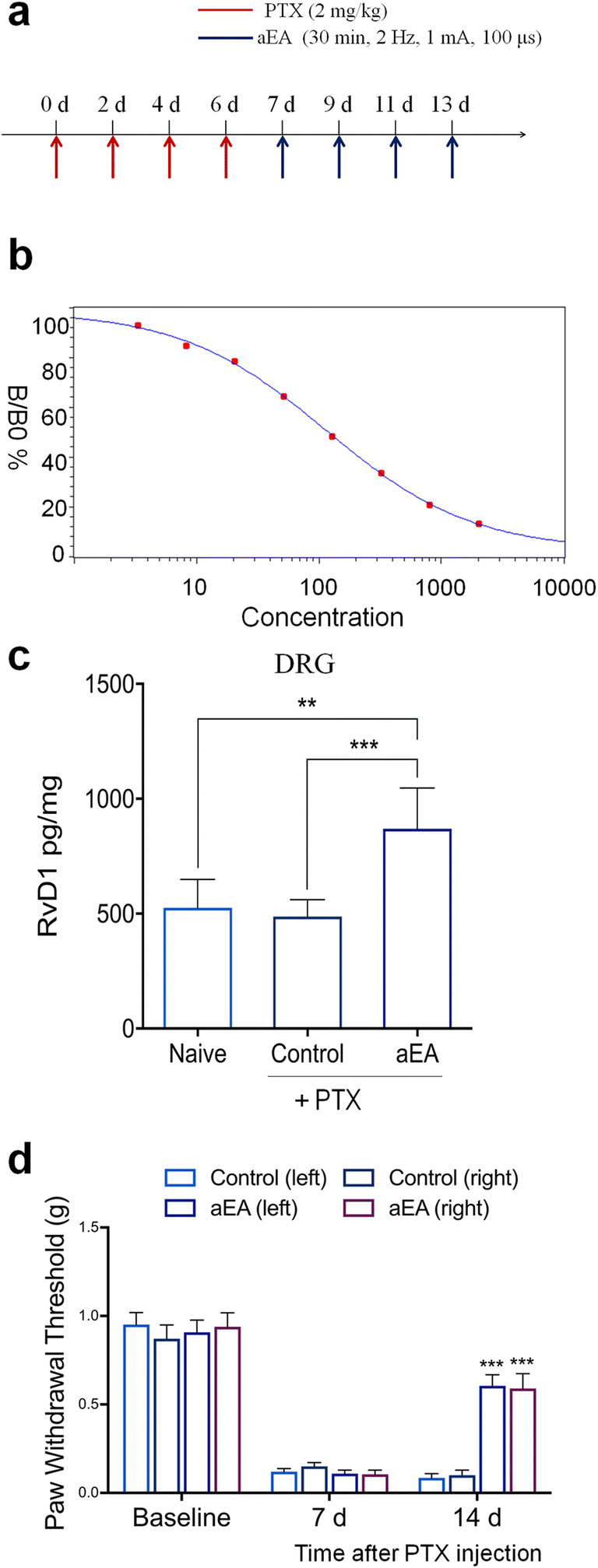
Auricular vagus nerve stimulation via EA (aEA) increases RvD1 in DRG tissue and reduces neuropathic pain after paclitaxel (PTX)-induced CIPN in mice. (a) Experimental paradigm for PTX treatment and unilateral aEA. (b) Standard curve of RvD1 ELISA. R = 0.999. (c) aEA increases RvD1 levels in DRG 14 days after PTX treatment. **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, one-way ANOVA with Bonferroni’s post hoc test, n = 6 mice per group. (d) aEA reduces mechanical allodynia 14 days after PTX treatment. *** P < 0.001 versus the control group without aEA. Two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni’s post hoc test, n = 10 mice per group. Methods for Fig. 2: Adult CD1 mice of both sexes (25–35 g) were purchased from Charles River Laboratories. All animals were maintained at the Duke University Animal Facility. Animal experiments were approved by the Animal Care Committee of Duke University. The location of auricular EA (aEA) is similar to human points given through two acupuncture needles on the core area of the right ear. The parameters of EA are 1 mA, 15 Hz, 0.1 ms pulse, and 30 min. To minimize stress during aEA, mice were lightly anesthetized mice with 1% isoflurane. aEA was given every other day for 1 week on days 7, 9, 11, and 13. To induce CIPN in mice, 4 intraperitoneal injections of paclitaxel (2 mg/kg per injection, Sigma) were given on days 0, 2, 4, and 6. For testing the mechanical pain threshold, the plantar surface of each hindpaw was stimulated with a series of von Frey fibers with logarithmically incrementing stiffness (0.02–2.56 g, Stoelting), presented perpendicular to the plantar surface. The 50% paw withdrawal threshold was calculated using Dixon’s up-down method [66]. All data were expressed as the mean ± SEM. All data were analyzed by one-way or repeated measures two-way ANOVA, followed by Bonferroni’s post hoc test. P < 0.05 was taken as statistically significant. Mouse RvD1 ELISA was conducted as previously described [67]. ELISA kit was purchased from Cayman Chemicals (Catalog number, 500380). The detection sensitivity of this ELISA kit is 15 pg/ml, which is sufficient to detect RvD1 levels in DRG samples. Lumbar DRG tissues from both sides were collected from naïve animals and animals 14 days after PTX treatment. DRGs were homogenized in a lysis buffer containing protease and phosphatase inhibitors. Tissue samples were centrifuged at 12,500×g for 10 min and the supernatant was collected. Protein concentrations were determined by BCA Protein Assay (Pierce). For each reaction in a 96-well plate, 100 μg of proteins of DRG samples were used. ELISA was performed according to the manufacturer’s protocol. The samples and the competition RvD1 tracer (RvD1 linked to acetylcholinesterase (AChE) were incubated overnight at 4 °C. The signal in the ELISA plate was developed by Ellman’s reagent, a substrate of AChE. The optical densities of samples were measured using an ELISA plate reader (Bio-Rad) at a wavelength of 420 nm and RvD1 levels were calculated using the standard curves. The standard curve was included in each experiment. The RvD1 values of the samples were in the linear range of the standard curve
