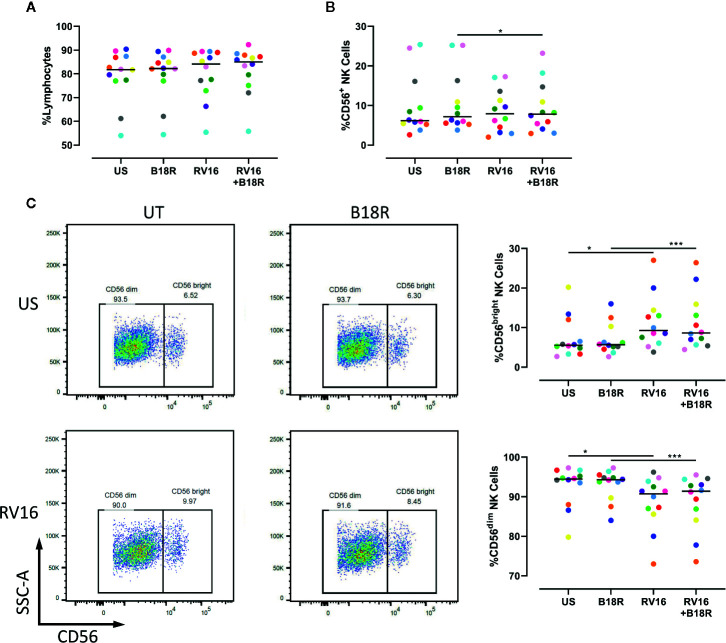
Figure 1.
RV16 altered NK cell populations, in an IFN-I independent manner. PBMCs from healthy people (n=12) were cultured in vitro with B18R (100 ng/ml) for 1 h to block IFN-I signaling, alongside a media-only control (UT), prior to stimulation with RV16 (MOI = 1), alongside an unstimulated control (US) for 24 h. (A) Percentage of lymphocytes, (B) total CD56+ NK cells, (C) and NK cell subsets (CD56dim and CD56bright) were evaluated using flow cytometry. Raw dot plots are representative of all 12 healthy donors. Each colored symbol represents data from one donor, lines represent medians. Data are representative of three experiments. *p<0.05, ***p<0.001 by Wilcoxon matched-pairs signed rank tests. RV16, rhinovirus 16; IFN-I, type I interferon; NK, natural killer; PBMC, peripheral blood mononuclear cell; UT, untreated; MOI, multiplicity of infection; US, unstimulated; SSC-A, side scatter-area.