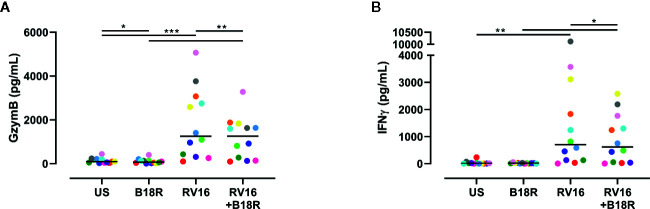
Figure 6.
RV16 stimulated PBMCs release GzymB and IFNγ; this occurs to a lesser extent when IFN-I signaling is blocked. PBMCs from healthy people (n=12) were cultured in vitro with B18R (100 ng/ml) for 1 h, prior to stimulation with RV16 (MOI = 1), alongside an unstimulated control (US) for 24 h. ELISAs were performed on cell-free supernatants to determine GzymB and IFNγ concentrations. (A) Concentration of GzymB released into cell culture media by PBMCs. (B) Concentration of for IFNγ released into cell culture media by PBMCs. Each colored symbol represents data from one donor, lines represent medians. Data are representative of three experiments. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001 by Wilcoxon matched-pairs signed rank tests. IFN-I, type I interferon; GzymB, granzyme B; IFNγ, interferon gamma; PBMC, peripheral blood mononuclear cell; RV16, rhinovirus 16; UT, untreated; MOI, multiplicity of infection; US, unstimulated; ELISA, enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay.