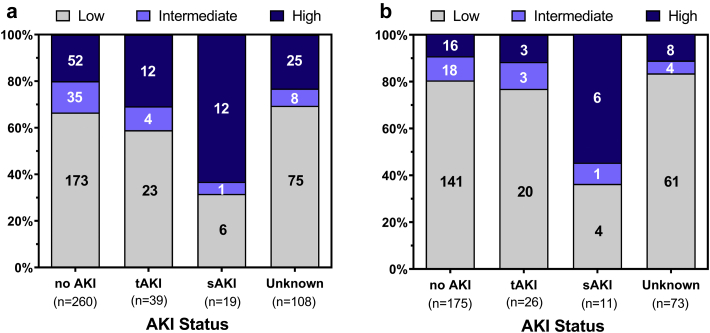
Figure 3.
Urinary neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (uNGAL) measured by dipstick correlates with sustained elevations in creatinine. (a) High uNGAL readings in the emergency department correlate with sustained serum creatinine elevation after admission (P = 0.004, n = 426). (b) The relationship was even more evident once confounders (baseline estimated glomerular filtration rate < 30 or positive urinary tract infection or unknown urinary tract infection status) were excluded (P = 0.008, n = 285). Light gray = low uNGAL, dark gray = intermediate uNGAL, and black = high uNGAL. AKI, acute kidney injury; DPI, dots per inch; sAKI, sustained acute kidney injury; tAKI, transient acute kidney injury; unknown, insufficient data to make categorization.