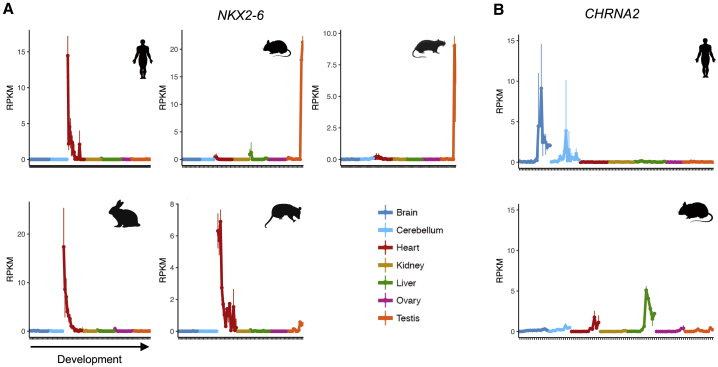
Figure 4.
Suitability of the Mouse as a Model
(A) Developmental profile of NKX2-6 in human, mouse, rat, rabbit, and opossum (marsupial). NKX2-6 is robustly expressed in the human heart, but not in mouse, and the conotruncal heart malformations observed in human are not recapitulated by a mouse knockout. The human heart profile of NKX2-6 is ancestral, as it is similar to the profiles in rabbit and opossum.
(B) Developmental profile of CHRNA2 in human and mouse. CHRNA2 is robustly expressed in the human brain, but not in mouse, and the epileptic phenotypes observed in human are not recapitulated by a mouse knockout.
In (A) and (B), the x axis shows samples for each organ ordered from early to late development (stages sampled in Table S4), and the y axis shows expression levels in reads per kilobase of exon model per million mapped reads (RPKM).