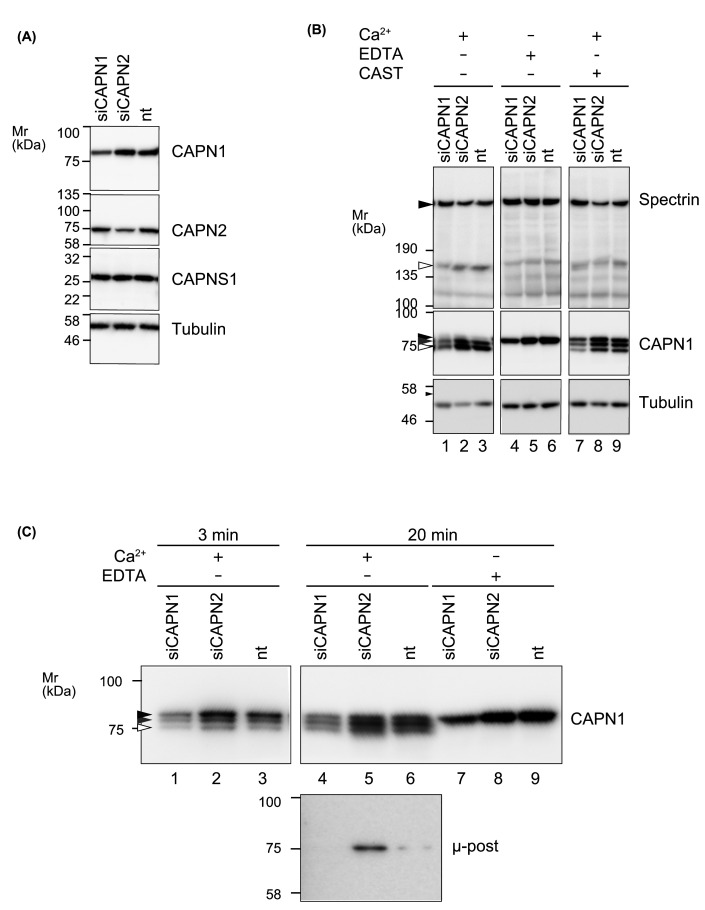
Figure 8. Modification of sequential autolysis of C1 in cultured cells.
(A) Isoform specific knockdown of calpains. HCT116 cells were transfected with siRNA targeting CAPN1 or CAPN2, or non-targeting siRNA (nt). After 48 h, expression levels of indicated proteins were analyzed by Western blot to confirm the efficiency and specificity of knockdown. Each lane contains 20 μg of proteins and tubulin was used as a loading control. (B) Activation-associated autolysis of C1. Lysates of siRNA-treated cells were treated with 5mM CaCl2 at 30°C for 20 min. Autolysis of C1 was detected as generation of two fragments, 78 kDa (gray arrowhead) and 76 kDa (open arrowhead), using anti-CAPN1 antibody. Arrowhead indicates pre-autolytic, full-length CAPN1 (80 kDa). When C2 was down-regulated by siRNA targeting CAPN2, attenuation of autolysis of C1 was detectable (lane 2 vs. 3, gray and open arrowheads). In the presence of 40 nM CAST-d1, autolysis of CAPN1 as well as proteolysis of spectrin was partially suppressed. Each lane contains 20 μg of proteins. (C) Effect of C2 on activation-associated autolysis of C1. Autolytic profiles of CAPN1 were further analyzed by performing another set of incubation using lysates from cells treated with indicated siRNAs. Down-regulation of C2 attenuated the decrease of pre-autolytic fragment of CAPN1 at 3 min (lane 2 vs. 3, arrowhead) and 76 kDa post-autolytic fragment at 20 min (lane 5 vs. 6, μ-post). Lanes contain 8 μg (1–3) and 16 μg (4–9) of proteins.