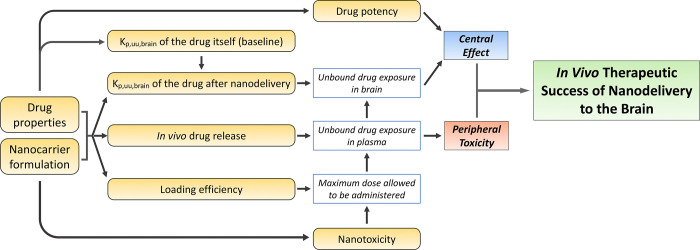
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of factors contributing to the in vivo therapeutic success of nanodelivery to the brain. The NC formulation in conjunction with drug properties could impact loading efficiency, in vivo drug release, and Kp,uu,brain of the drug. Whether or not nanotoxicity occurs is dependent on the NC formulation used. Drug-specific properties like Kp,uu,brain and potency are important. The Kp,uu,brain of the drug itself will determine whether and how much the brain delivery can be improved by nanodelivery. Both loading efficiency and nanotoxicity have an impact on the maximum dose allowed to be administered, which will further influence unbound drug exposure in plasma and brain. In vivo drug release will affect unbound drug exposure in plasma. The Kp,uu,brain of the drug after nanodelivery will influence how high the unbound brain exposure could be. Unbound brain exposure, together with drug potency, will determine the drug effect in the CNS. Drug-induced peripheral side effects are associated with unbound drug exposure in plasma. It is the central effect and peripheral side effect combined that determine the therapeutic success of nanodelivery to the brain.