Figure 7.
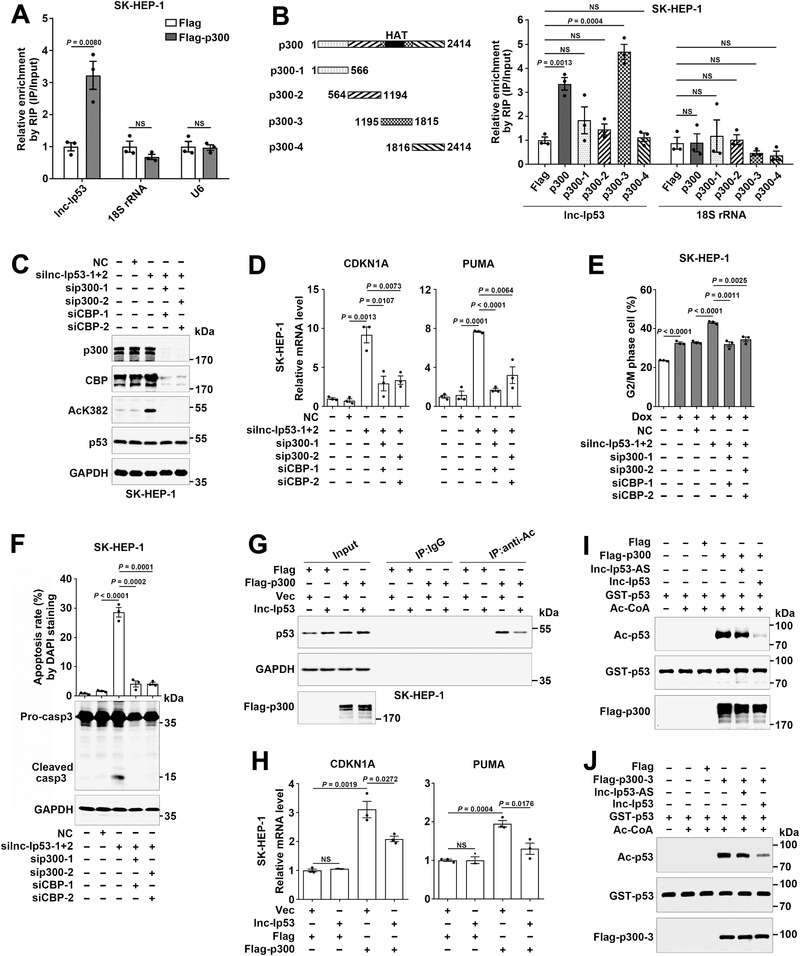
Lnc‐Ip53 associates with p300 and attenuates its activity to acetylate p53. A,B) Lnc‐Ip53 interacted with the 1195‐1815‐aa region of p300 in vivo. Cells expressing Flag or Flag‐tagged p300 fragments were subjected to RIP using anti‐Flag affinity gel, followed by qPCR for lnc‐Ip53 and negative control genes (18S rRNA, U6). C) Silencing p300/CBP (sip300/CBP) attenuated silnc‐Ip53‐stimulated p53 acetylation. Cells were transfected with the indicated RNA duplexes for 42 h, then incubated with 5 µM SAHA for 6 h before immunoblotting for K382‐acetylated p53. D–F) sip300/CBP abrogated the stimulatory effect of silnc‐Ip53 on D) CDKN1A/PUMA expression, E) G2/M arrest, and F) apoptosis. Cells were transfected with the indicated RNA duplexes for 52 h before qPCR (D), or for 39 h, and then incubated with 0.1 µM Dox for 9 h before cell cycle analysis (E), or transfected with the indicated RNA duplexes for 72 h before DAPI staining or 68 h before immunoblotting (F). G) Lnc‐Ip53 attenuated p300‐promoted p53 acetylation. Cells were incubated with 5 µM SAHA for 6 h, followed by IP using IgG or antibody against acetyl lysines (anti‐Ac) and then immunoblotting for p53. H) Lnc‐Ip53 attenuated p300‐induced CDKN1A/PUMA expression. For (G,H), cells infected with control lentiviruses (Vec) or lentiviruses expressing the indicated molecules were used. I,J) The in vitro acetylation assays revealed that lnc‐Ip53 impaired p300 or p300‐3‐mediated p53 acetylation. The purified Flag, I) Flag‐p300 or J) Flag‐p300‐3 proteins were preincubated with lnc‐Ip53 or lnc‐Ip53‐AS, followed by addition of recombinant GST‐p53 and acetyl coenzyme A (Ac‐CoA). The level of acetylated‐p53 was analyzed by immunoblotting using antibody against acetyl lysines (anti‐Ac). + or −, cells with (+) or without (−) the indicated treatment. Data are shown as mean ± SEM of three independent experiments; p‐values were determined by unpaired Student′s t‐test; NS, not significant.
