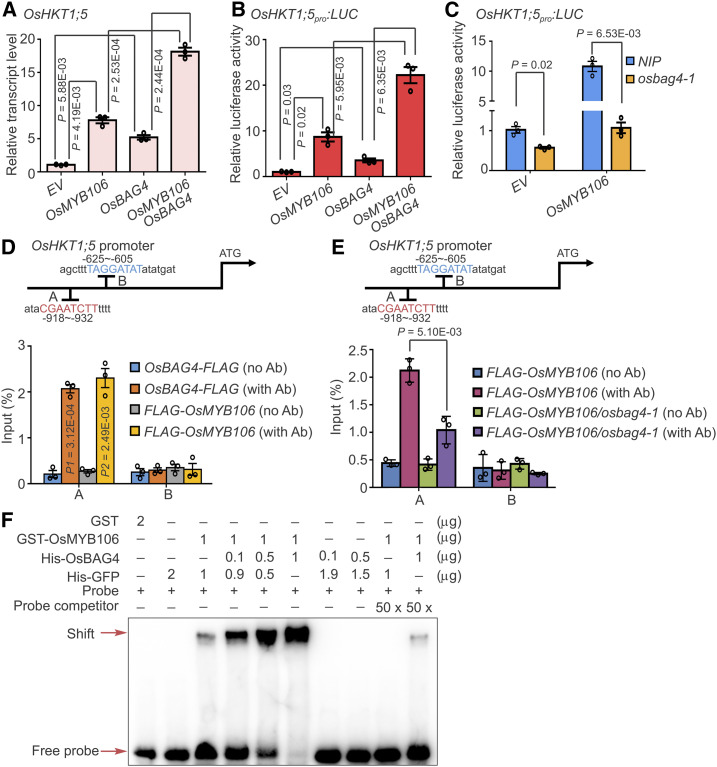
Figure 6.
OsBAG4 Is Required for OsMYB106 Activity.
(A) to (C) OsBAG4 positively impacts the transcriptional activation activity of OsMYB106. (A) 35Spro:GFP (EV), 35Spro:FLAG-OsMYB106 (OsMYB106), 35Spro:OsBAG4-FLAG (OsBAG4), or 35Spro:FLAG-OsMYB106 (OsMYB106) together with 35Spro:OsBAG4-FLAG (OsBAG4) were transfected into NIP root protoplasts. After 6-h incubation, OsHKT1;5 expression levels were measured by RT-qPCR. (B) The OsHKT1;5pro:LUC construct together with UBQ10pro:GUS was cotransfected with 35Spro:GFP (EV), 35Spro:FLAG-OsMYB106 (OsMYB106), 35Spro:OsBAG4-FLAG (OsBAG4), or 35Spro:FLAG-OsMYB106 (OsMYB106) and 35Spro:OsBAG4-FLAG (OsBAG4) into NIP root protoplasts. After incubation for 20 h, luciferase and GUS activities were measured. After normalizing LUC activity against GUS activity, promoter activities of different samples were normalized against the promoter activity of the EV sample. (C) The OsHKT1;5pro:LUC construct together with UBQ10pro:GUS was cotransfected with either 35Spro:GFP (EV) or 35Spro:FLAG-OsMYB106 (OsMYB106) into NIP or osbag4-1 root protoplasts. After incubation for 20 h, luciferase and GUS activities were measured. After normalizing LUC activity against GUS activity, promoter activities of different samples were normalized against the promoter activity of the EV sample. The EV construct was used as a control. Data represent means ± sd (n = 3, transfection experiments were performed three times). Individual values (black circles) are shown. Statistical analysis was performed by Student’s t test (see [A] to [C]).
(D) Results of ChIP-qPCR showing that OsBAG4 and OsMYB106 bound to the A site (fourth cis-element displayed in Figure 5A). Anti-FLAG antibody was used to perform ChIP-qPCR on roots of OsBAG4pro:OsBAG4-FLAG and OsMYB106pro:FLAG-OsMYB106 complementation lines (OsBAG4-FLAG and FLAG-OsMYB106). The B site (fifth cis-element displayed in Figure 5A) was a negative control. Error bars indicate ± sd (n = 3, three biological replicates of ChIP experiments were performed for ChIP-qPCR). Individual values (black circles) were shown. Statistical analysis was performed by Student’s t test. Ab, antibody.
(E) Results of ChIP-qPCR showing that OsBAG4 impacts the affinity of OsMYB106 for the consensus cis-element in OsHKT1;5 promoter in vivo. ChIP with anti-FLAG antibody was performed on roots of F2 plants obtained by crossing OsMYB106pro:FLAG-OsMYB106 with NIP or osbag4-1 mutant (FLAG-OsMYB106 or FLAG-OsMYB106/osbag4-1). Specific primers for A and B sites were used for qPCR, and the B site was used as a negative control. Primers are listed in Supplemental Data Set 14. Error bars indicate ±sd (n = 3, three biological replicates of ChIP experiments were performed for ChIP-qPCR). Individual values (black circles) are shown. Statistical analysis was performed by Student’s t test.
(F) Results of EMSA showing that OsBAG4 impacts OsMYB106 binding affinity to the cis-element in OsHKT1;5 promoter in vitro. Different combinations of proteins were incubated with biotin-labeled probes at the 5′ end of single strand. His-GFP was used to normalize for total protein level.