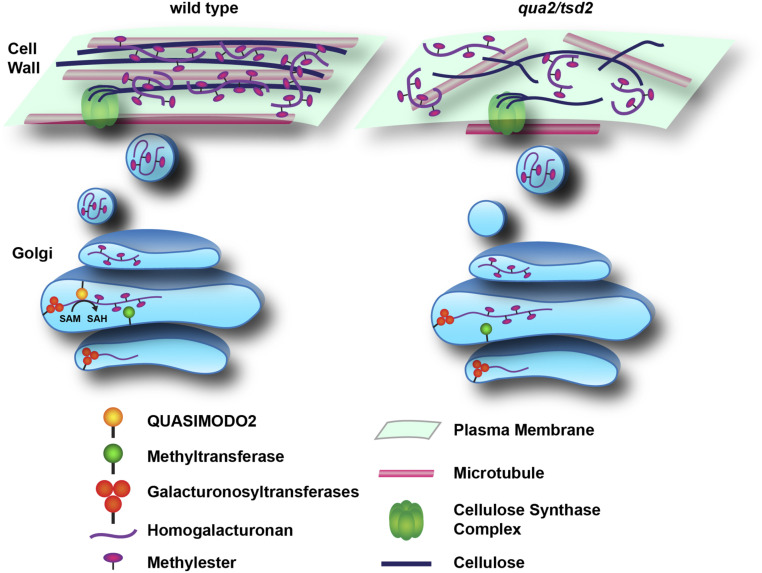
Figure 8.
Schematic of How Loss of the Pectin Methyltransferase QUA2 Affects HG Biosynthesis, Cellulose Biosynthesis, and Wall Architecture.
In wild-type plants (left), QUA2 functions as a methyltransferase to help synthesize highly methylesterified HG. qua2 and tsd2 mutants (right) produce lower amounts of HG and accumulate less HG in the cell wall, which influences the activity of plasma membrane-localized CSCs guided by cortical microtubules, decreasing cellulose deposition in the wall. The reduced HG content in the wall also alters cellulose microfibril patterning. The disruption of wall structure due to lower pectin and/or cellulose alters microtubule patterning and enhances the molecular mobility of pectin and cellulose, possibly due to increased interactions between them.