Figure 20.
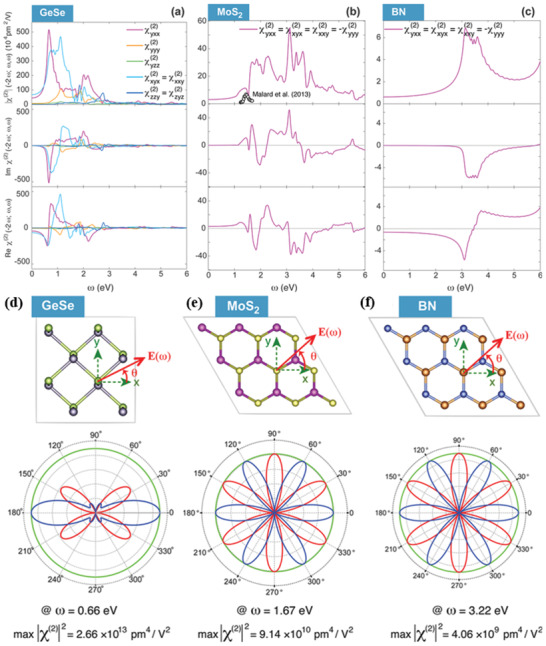
The magnitude, imaginary, and real component of SHG susceptibility for: a) a GeSe monolayer which has seven nonzero susceptibility tensor elements, b) a MoS2 monolayer which has four independent SHG elements, and c) a h‐BN monolayer with only one independent element. Black dots indicate the experimental values. d–f) Polarization anisotropy of SHG susceptibilities in monolayer GeSe, MoS2, and h‐BN. The red/blue solid lines are the polarization components of the SHG response parallel/perpendicular to the polarization of the incident electric field E(ω). θ is the rotation angle between E(ω) and the crystal lattice. Reproduced with permission.[ 52 ] Copyright 2018, American Chemical Society.
