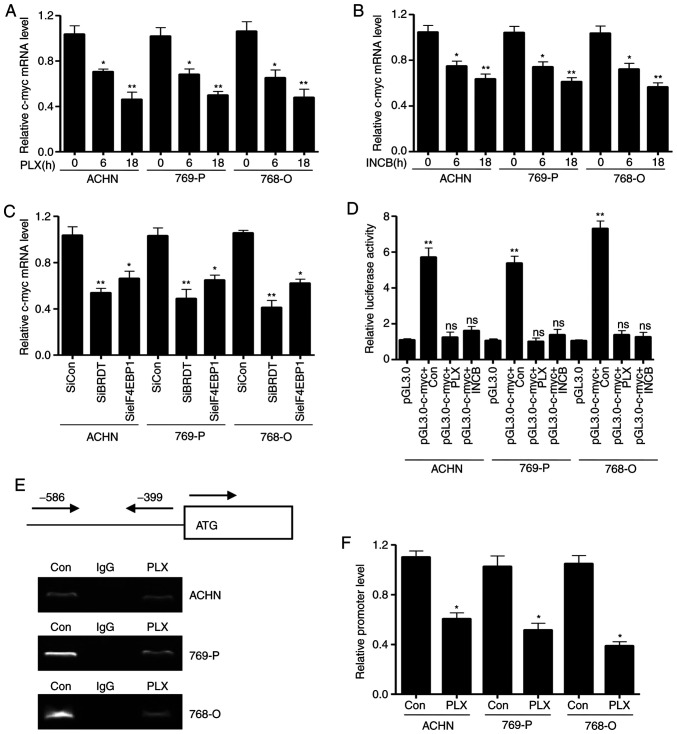
Figure 5.
Bromodomain and extraterminal domain inhibitors decrease eIF4EBP1 associated with c-myc promoter. The three cell lines were treated with the indicated concentrations of (A) PLX51107 or (B) INCB054329 for different time periods (0, 6 and 18 h) and subjected to RT-qPCR. (C) The three cell lines were transiently transfected with the indicated siRNAs or control siRNAs for 24 h. Total RNA was extracted and subjected to RT-qPCR assay for detecting the c-myc mRNA transcription level. (D) The three cell lines were transiently transfected with c-myc promoter plasmid or the control vector using Exfect reagent and treated with the indicated concentrations of PLX51107 or INCB054329 for 36 h. Renilla plasmids were co-transfected as the loading control. The cells were lysed and subjected to dual luciferase reporter assays. The three cell lines were treated with PLX51107 for 36 h, and then subjected to chromatin immunoprecipitation using eIF4EBP1 antibody. The c-myc promoter was detected using primers designed from −586 to −399 pre-leading regions of the start site (0 is the ATG start site). The PCR products of c-myc promoter was analyzed by (E) and agarose gel electrophoresis and (F) qPCR. Data are representative of three independent experiments. Bars represent the standard deviation. *P<0.05 and **P<0.01. RT-qPCR, reverse transcription-quantitative PCR; PLX, PLX51107; INCB, INCB054329; Con, control; siRNA, small interfering RNA; siCon, control siRNA; BRDT, bromodomain testis-specific protein; eIF4EBP1, eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E-binding protein 1.