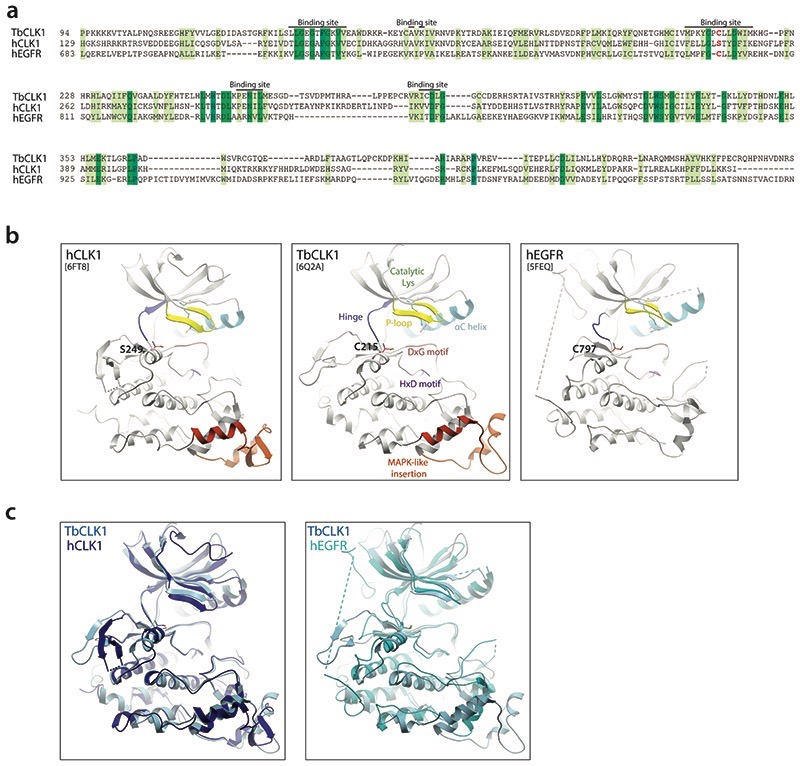
Extended Data Fig. 5. Similarity of hEGFR and CLK1 binding sites highlighting potential of AB1 to covalently bind to TbCLK1.
(a) Sequence alignment of hEGFR (Uniprot id: P00533), hCLK1 (Uniprot id: P49759) and TbCLK1 show similarity in binding site residues with presence of covalent cysteine (red) in TbCLK1 explaining selectivity over hCLK1.
(b) Comparison of ribbon diagram x-ray crystal structure of hCLK1 (PDB: 6FT8), TbCLK1 (PDB: 6Q2A), and hEGFR (5FEQ). The kinase components are coloured and labelled in TbCLK1 (middle panel). Note the conservation of cysteine in the kinase domain in TbCLK1 (C215) and hEGFR (C797), whereas in the same position, hCLK1 has serine 249.
(c) An overlay of TbCLK1 with hCLK1 (left) and hEGFR (right) structures.