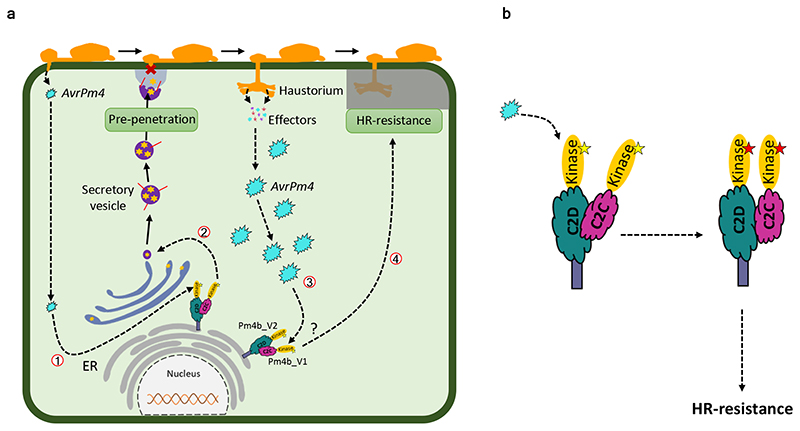
Fig. 6. A possible working model of Pm4-mediated resistance.
a, A schematically drawn wheat epidermal cell attacked by a mature powdery mildew germling. An early release of small amounts of effectors at around 12 hours translates ① into induction of Pm4b-dependent pre-haustorial resistance ②. Later, when large amounts of effectors are present ③, the recognition of AvrPm4 (light blue) by Pm4b protein complex will lead to Pm4b-mediated hypersensitive response (HR) ④. ER, endoplasmic reticulum. b, Schematic model of a possible activation mechanism of Pm4 upon a hypothetical AvrPm4 recognition. In the absence of the AvrPm4, Pm4_V1 and Pm4_V2 are in a resting state, forming a heterocomplex interacting via C2 domains. This heterocomplex is anchored into the membrane of the ER and it is inactive (yellow star in the S_TKc domains). Upon AvrPm4 recognition by the C2C/D or the kinase domains the heterocomplex undergoes conformational changes, leading to activation of the kinase activity (red star in the S_TKc domains) and disease resistance. Numbers indicate the sequence of steps of the proposed model.