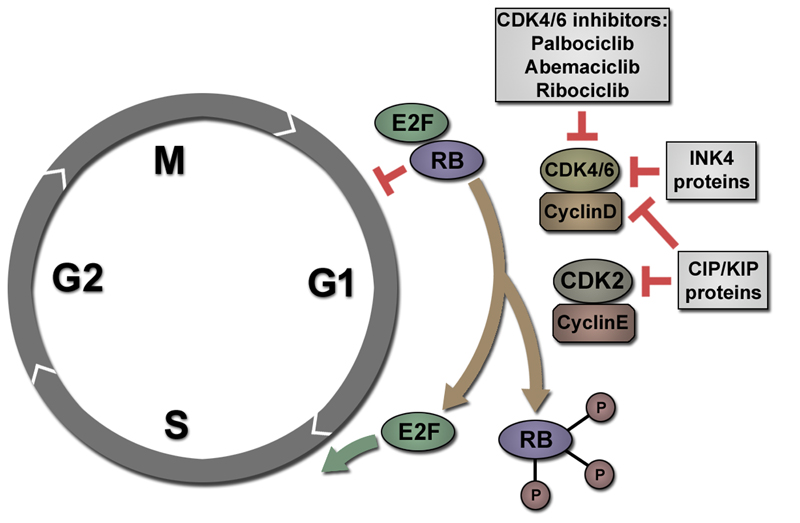
Figure 1. Inhibition of CDK4/6 induces cell cycle arrest in G1 phase.
After M phase, RB is hypophosphorylated and can bind and inhibit transcription factors of the E2F family. When activated by Cyclin D, CDK4/6 phosphorylate RB. RB can subsequently be phosphorylated by CDK2/Cyclin E. Hyperphosphorylated RB releases E2F transcription factors that activate a transcriptional programme promoting transition to S phase. Cyclin dependent kinase inhibitors of the CIP/KIP family (such as p21CIP) can inhibit both CDK2 and CDK4/6 activity. INK4 proteins, like p16INK4a, specifically inhibit CDK4/6 activity leading to cell cycle arrest in G1 phase. CDK4/6 inhibitors (such as Palbociclib, Abemaciclib or Ribociclib) exert similar effects, also inducing an arrest in G1.