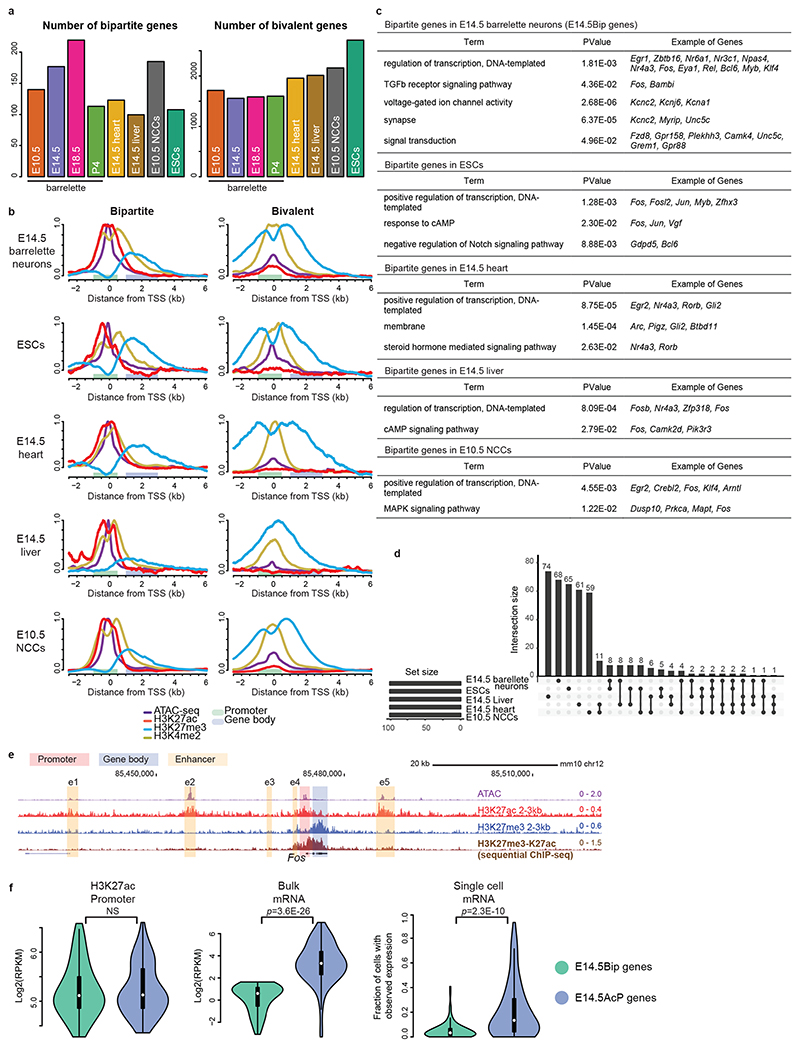
Fig. 2. Developmental cellular representation and genome-wide distribution of bipartite chromatin, and promoter H3K27ac and gene body H3K27me3 coexistence at bipartite genes.
a, Estimated numbers of bipartite (left) and bivalent (right) genes in E10.5 K20tdTomato/+ progenitors, E14.5, E18.5 and P4 Drg11vPrV-ZsGreen/+ barrelette neurons, E14.5 mouse heart tissue, E14.5 mouse liver tissue, E10.5 neural crest-derived cells (NCCs), and mouse embryonic stem cells (ESCs). b, Aggregate plots of chromatin features (ATAC-seq, ChIP-seq, as indicated) around the transcription start site (TSS) of bipartite (left) and bivalent genes (right) in the distinct developing cell types, as indicated. Promoters and gene bodies are highlighted; Y axes of bipartite and bivalent plots are scaled so that the two plots can be directly compared with each other for the same mark (Methods). c, Gene Ontology of bipartite genes identified in the different developing cell types. d, Upset plot showing intersections among bipartite genes in different developing cell types. Bipartite genes are mostly tissue- and stage-specific with only a few shared. In b-d, top 100 bipartiteness scored genes are used, as a conservative definition of bipartite genes. e, Genome browser of bipartite Fos displaying accessibility (ATAC-seq), 2-3-kb fragment H3K27ac and H3K27me3 single ChIP-seq, and H3K27me3/H3K27ac sequential ChIP-seq from E14.5 hindbrain. H3K27me3 and H3K27ac coexist on gene body and promoter, respectively (Supplementary Note). f, Violin plots displaying promoter H3K27ac (left), bulk mRNA-seq levels (middle, Smart-seq2), and single-cell fractions with detected mRNA transcripts (right, 10X Genomics) in E14.5 barrelette neurons; E14.5 bipartite genes (E14.5Bip, green, n = 97) and E14.5 non-bipartite genes with Bip-matching promoter H3K27ac levels (E14.5AcP genes, blue, n = 97) are compared (Supplementary Note; Methods). Plots extend from the data minima to the maxima with the white dot indicating median, the box showing the interquartile range and whiskers extending to the most extreme data point within 1.5× the interquartile range. P values are from two-sided Wilcoxon’s tests. NS: not significant (P > 0.05).