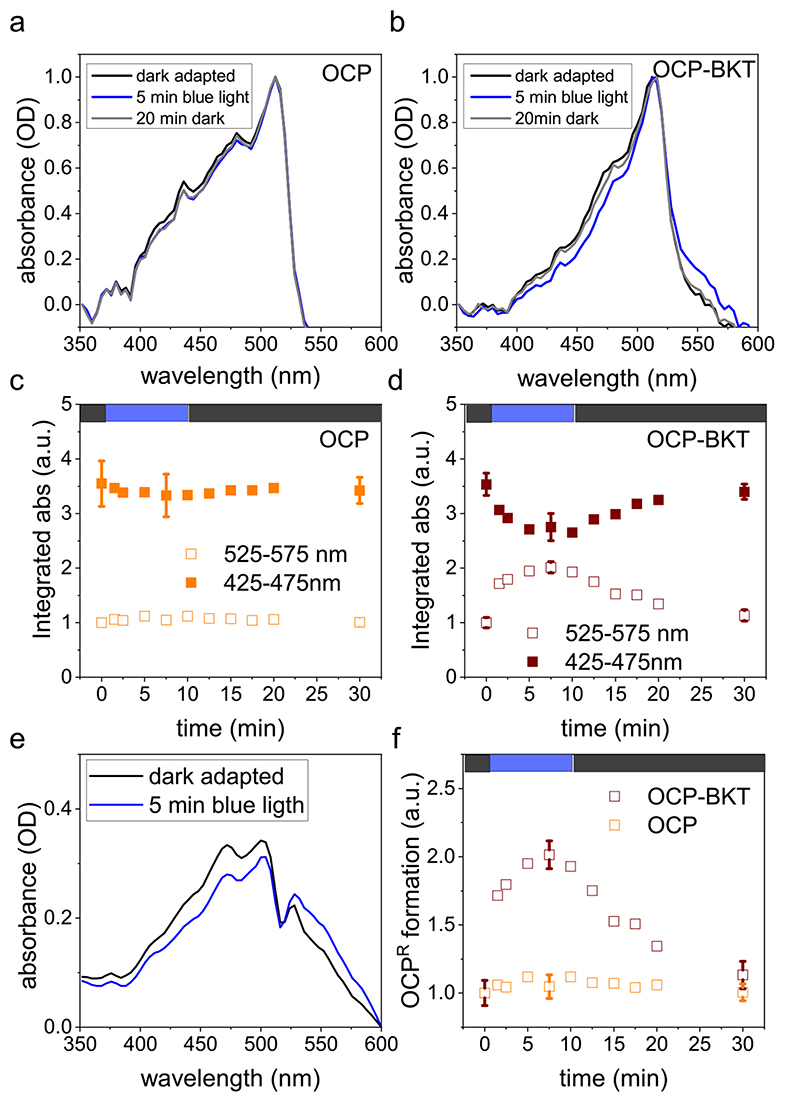
Fig. 5. Blue light excitation of OCP proteins.
a) b) Absorption spectra of recombinant OCP Orange Carotenoid-binding Protein) isolated from transformed Chlamydomonas rein-hardtii strains expressing OCP only (ocp1 a, OCP) or both BKT (β-carotene ketolase) and OCP (ocp1-bkt1 b, OCP-BKT). Absorption spectra are reported as optical density (OD) for dark-adapted protein (black), after 5 min of blue light illumination (blue) and after 20 min of dark recovery (grey). c) d) Absorption spectra integrated in 525–575 nm range (active OCPR) or 425–475 nm range (inactive OCPO) reported as arbitrary units (a.u.). e) Absorption spectra of OCP-BKT after subtraction of YFP (Yellow Fluorescent Protein) signal for dark adapted sample and after 5 min of blue light illumination. f) Comparison of OCPR formation (spectra integrated in 525–575 nm range) for OCP and OCP-BKT. Integrated absorption data reported in c), d) and f) were normalized to 1 in the case of 525–572 nm absorption of dark-adapted samples (time 0). Error bars are reported as standard deviation in c), d) and f) for dark adapted samples, after the blue light treatment and after dark recovery (n = 3).