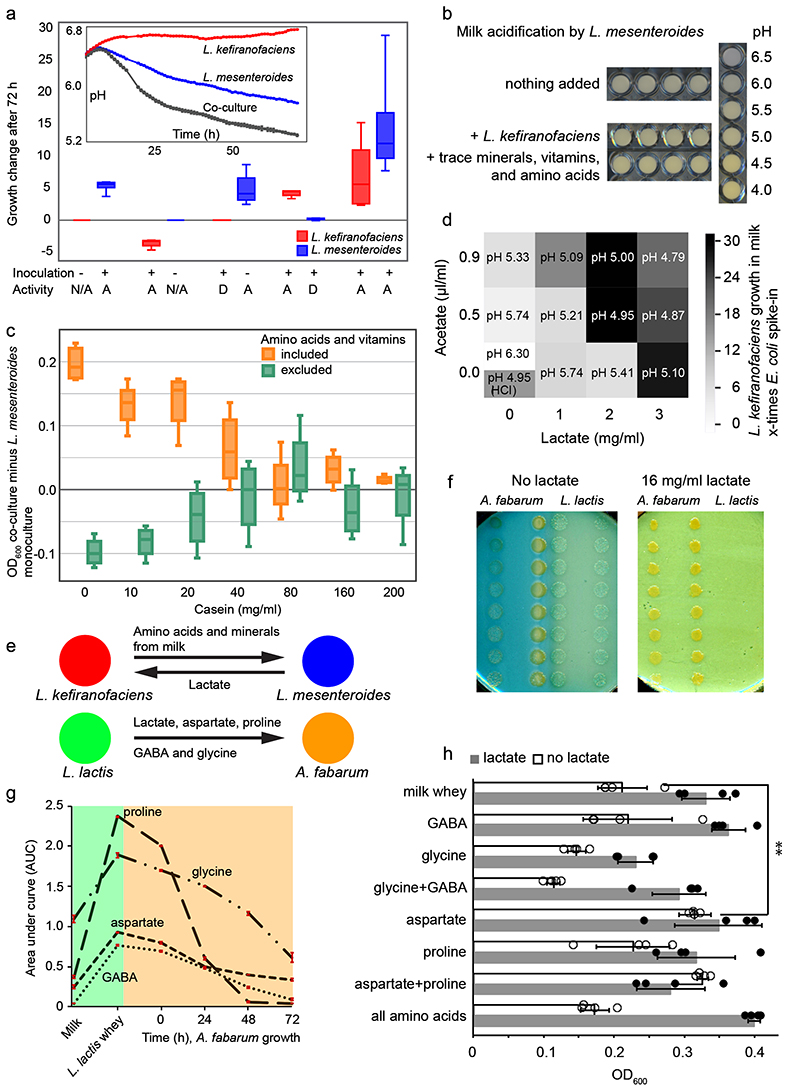
Fig. 5. Unraveling selected metabolic interactions in kefir.
a, L. kefiranofaciens and L. mesenteroides benefit from each other when both species are alive. While L. kefiranofaciens benefits from dead L. mesenteroides, L. mesenteroides only profits from live L. kefiranofaciens. D=dead (heat or ethanol treated), A=alive, N/A=not present. N=4, biologically independent samples; the boxplot represents the interquartile range including the median, and the ends of the whiskers represent ±1.5× interquartile range. b, Addition of amino acid mix, vitamin mix, and trace minerals enhances milk acidification by L. mesenteroides in a way comparable to co-culture with L. kefiranofaciens. c, Difference between L. mesenteroides growth in monoculture and its co-culture with L. kefiranofaciens underlines the role of proteolytic activity in the interaction between these two species. Shown are the data based on growth (OD600) in milk whey enriched with amino acids, vitamins, and varying amounts of casein peptides. N=4, biologically independent samples; the boxplot represents the interquartile range including the median, and the ends of the whiskers represent ±1.5× interquartile range. Grey shaded boxes, separators between adjacent casein peptide levels. d, Supplementation of lactate and acetate in various proportions supports the growth of L. kefiranofaciens in milk by a combination of lowering pH (which alone improves growth at pH 4.95, adjusted with HCl) and increasing lactate availability. Acetate supplementation does not exceed the effect of pH alone (N=4, biologically independent samples). e, Metabolites exchanged between L. kefiranofaciens and L. mesenteroides and between A. fabarum and L. lactis. f, Growth of A. fabarum and L. lactis on milk agar plates with and without lactate supplementation (16 mg/ml) suggests lactate cross-feeding. g, Aspartate, proline, glycine, and GABA are cross-fed between L. lactis and A. fabarum (N=3; error bars, standard deviation). h, Acetobacter growth in milk whey, and in milk whey plus 8 mg/ml lactate, supplemented with various amino acids and GABA. Lactate additionally boosts Acetobacter growth in all cases except aspartate (and aspartate plus proline) supplementation. N=4; error bars, standard deviation; **p=0,0054 (two-sided t-test). Data for Fig. 5c, d and h can be found in Supplementary Tables 21, 22 and 23, respectively. Data are presented as mean values +/- SD.