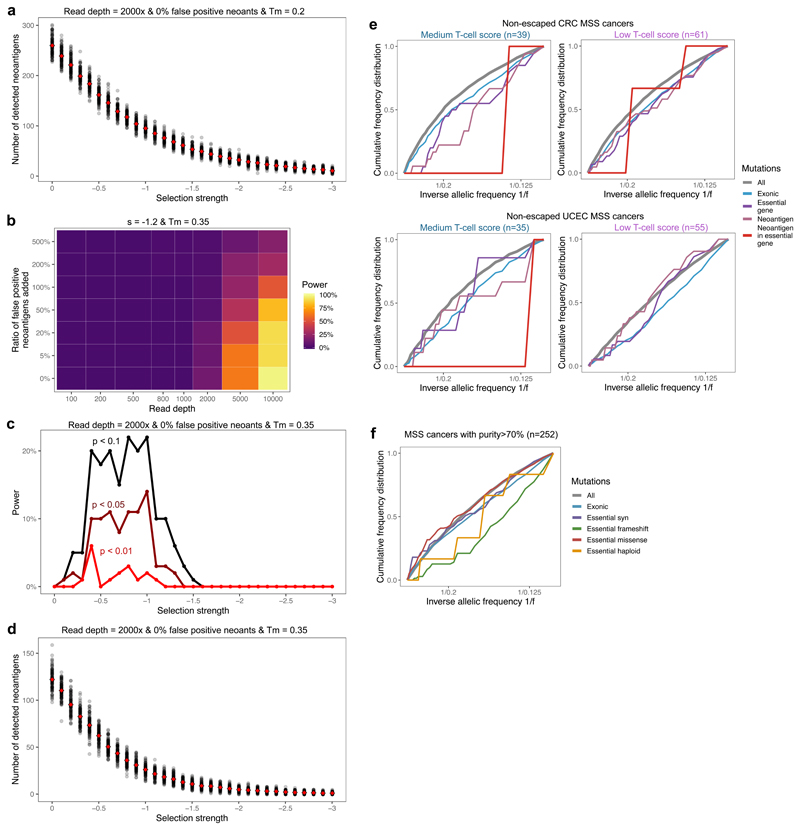
Extended Data Fig. 5. Detection of negative selection in variant allele frequency distribution.
(a) Number of detected (true) neoantigens in n=100 simulated tumours for each selection strength between s=0 and s=-3. The mean number detected at each selection value is shown in red. (b-d) Power (detection rate) to identify negative selection using two-sided Kolmogorov-Smirnov test (b-c) and number of detected neoantigens (d) as a function of read depth, false positive neoantigens amongst antigenic mutations and selection strength, when only mutations above the mutation-antigenicity threshold (Tm) of 0.35 are analysed as antigenic, instead of 0.2 (c.f. Figures 4c–d, Extended Data Figs. 4 & 5a). n=100 simulated tumours are used in the computation. (e) Cumulative VAF distribution of mutations detected in low and medium immune infiltrated CRC (upper panel) and UCEC (lower panel) MSS cancers without immune escape. VAF distributions of STAD sample could not be established due to low sample and mutation numbers. (f) Cumulative VAF distributions of mutations detected in essential genes in all TCGA MSS cancers with good tumour cellularity (above 70%). The curves show synonymous (purple), frameshift and nonsense (green), missense (red) and hemizygous (located in haploid regions of the genome, yellow) mutations found in essential gene exons.