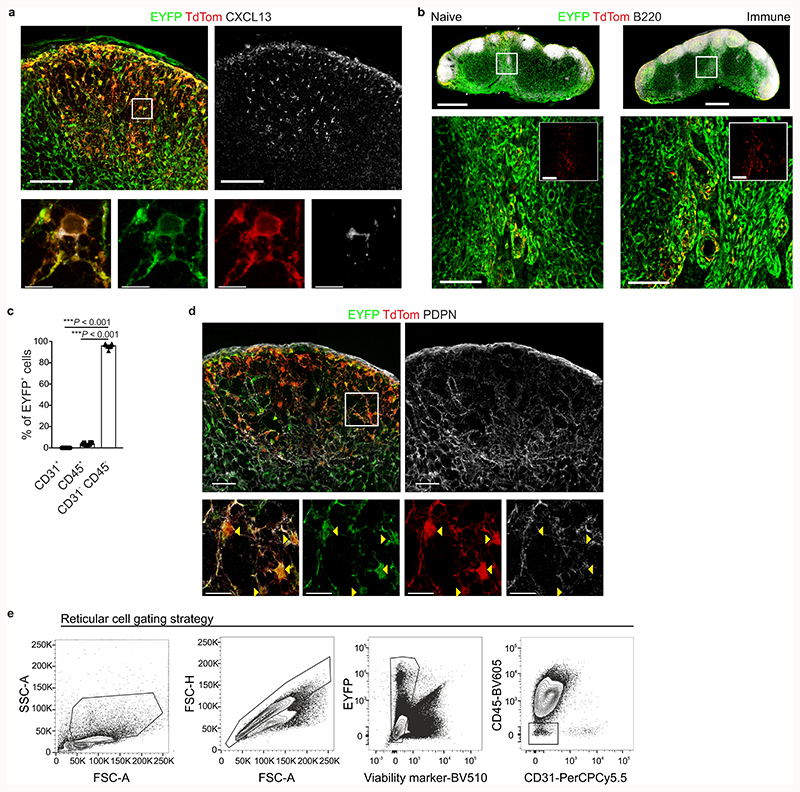
Extended Data Fig. 1. The Cxcl13-Cre/TdTom transgene faithfully demarcates non-endothelial, non-hematopoietic, CXCL13-expressing cells.
a, Representative immunofluorescence images of EYFP, TdTom, and CXCL13 expression in naive Cxcl13-Cre/TdTom EYFP mice. Scale bars, 100 μm and 10 μm. b, Representative images of TdTom expression in the medullary cords of naive and day 12 VSV-immunized Cxcl13-Cre/TdTom EYFP mice. Scale bars, 500 μm and 100 μm. c, Quantification of the percentage of EYFP+ cells expressing CD31 or CD45 in naive Cxcl13-Cre/TdTom EYFP mice. Mean and SEM are depicted. d, Representative images of EYFP, TdTom and podoplanin (PDPN) expression in naive Cxcl13-Cre/TdTom EYFP mice. Arrows point to the cell body. Scale bars, 50 μm and 20 μm. e, Flow cytometric gating strategy of non-hematopoietic, non-endothelial reticular cells from Cxcl13-Cre/TdTom EYFP mice. (a,b,d) Images are representative of at least five mice. (c,e) N = 8 naive mice, 4 independent experiments; P values as per one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparisons test.