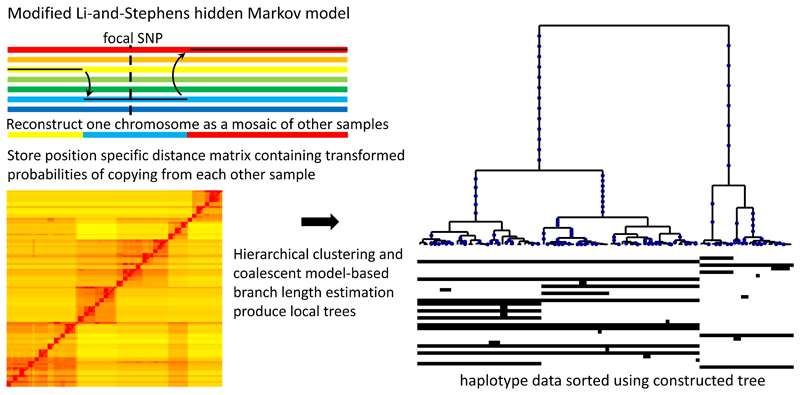
Figure 1. Relate method overview.
Our method applies a version of the Li-and-Stephens hidden Markov model15, modified to take ancestral and derived states into account, to calculate at a focal SNP (dotted vertical line) a position-specific distance matrix d (bottom left). Each entry dij of this matrix stores the rescaled loglikelihood of generating haplotype i by copying from haplotype j, which can be interpreted as the number of mutations carried by i, but not by j, locally around the focal SNP. (Methods; Supplementary Note). Our tree builder uses the resulting inferred distance matrix to coalesce haplotypes (right-hand side). After mapping mutations to their corresponding branches, we estimate branch lengths using an MCMC algorithm that employs a coalescent prior model.