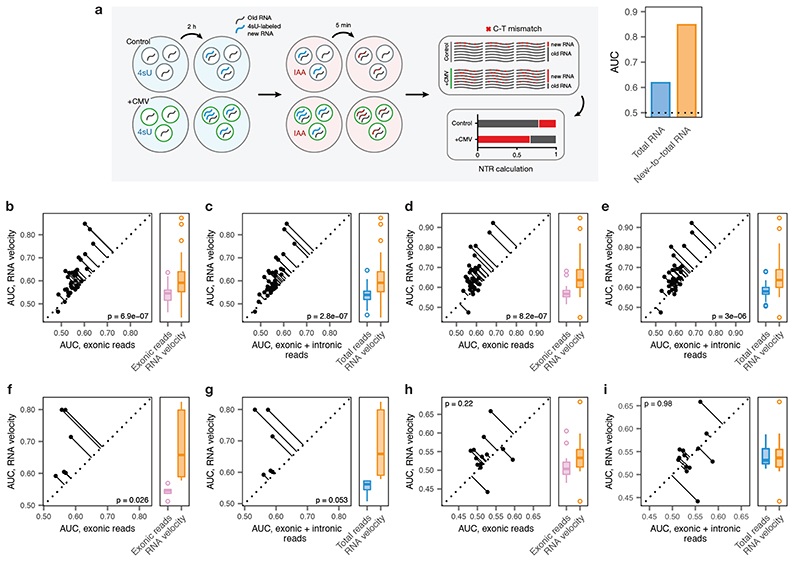
Extended Data Fig. 5. Cell type prioritization from transcriptional dynamics in acute experimental perturbations.
a, Left, schematic overview of the scSLAM-seq8 workflow. Cells are exposed to the nucleoside analogue 4-thiouridine (4sU), which is incorporated during transcription and converted to a cytosine analogue by iodoacetamide prior to RNA sequencing. This labeling permits in silico deconvolution of RNA molecules transcribed before and after 4sU exposure (‘old’ and ‘new’, respectively), and calculation of the ratio of new to total RNA (NTR), an experimental analogue to the computationally determined ‘RNA velocity’8,9. Right, AUCs for mouse fibroblasts exposed to lytic mouse cytomegalovirus (CMV) at 2 h post-infection, calculated by applying Augur to either total RNA or the NTR. The greater separability for the NTR reflects additional information specifically captured by the temporal dynamics of RNA expression in the context of this acute perturbation8.
b-e, Cell type prioritization based on exonic reads, total RNA, or RNA velocity for cells of the mouse visual cortex after exposure to light for 1 h, b-c, or 4 h, d-e, in the Hrvatin et al., 2018 dataset5. The AUC is significantly higher for RNA velocity than for either exonic reads (1 h, n = 34 cell types, 4 h, n = 35 cell types; two-sided paired t-tests: b, 1 h, p = 6.9 × 10-7; d, 4 h, p = 8.2 × 10-7) or total RNA (c, 1 h, p = 2.8 × 10-7; e, 4 h, p = 3.0 × 10-6), reflecting additional information specifically captured by acute transcriptional dynamics.
f-g, Cell type prioritization based on exonic reads, total RNA, or RNA velocity in an Act-seq10 dataset, which minimizes transcriptional changes induced by single-cell dissociation. Cell types of the medial amygdala in mice subjected to 45 min of immobilization stress and control mice were profiled by Drop-seq11 after treatment with the transcription inhibitor actinomycin D. The AUC is higher for RNA velocity than for either exonic reads (f, p = 0.026, n = 6 cell types) or total RNA (g, p = 0.053), reflecting the additional information specifically captured by acute transcriptional dynamics, and indicating this is not an artefact related to the transcriptional perturbations known to be induced by conventional dissociation procedures12.
h-i, Cell type prioritization based on exonic reads, total RNA, or RNA velocity in a chronic perturbation. Cell types of the lateral hypothalamic area were profiled by Drop-seq11 in mice after 9-16 weeks of maintenance on either high-fat diet or control diet13. No significant difference in AUCs was observed for RNA velocity compared to either exonic reads (h, p = 0.22, n = 13 cell types) or total RNA (i, p = 0.98), consistent with the time scale of the experimental perturbation.