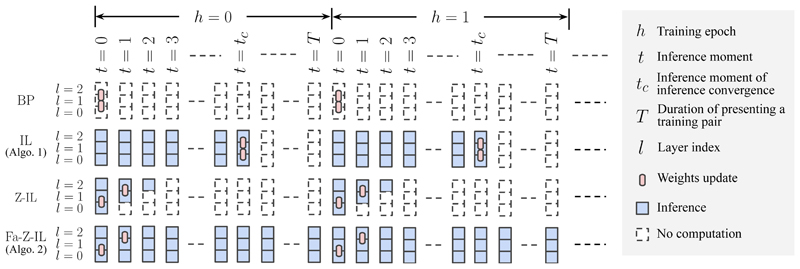
Figure 2.
Comparison of the temporal training dynamics of BP, IL, Z-IL, and Fa-Z-IL. We assume that we train the networks on a pair (s̅ in, s̅ out) from the dataset, which is presented for a period of time T, before it is changed to another pair, moving to the next training epoch h. Within a single training epoch h, (s̅ in, s̅ out) stays unchanged, and t runs from 0. As stated before, t is the time axis during inference, which means that IL (also Z-IL and Fa-Z-IL) in PCNs run inference starting from t = 0. The squares and rounded rectangles represent nodes in one layer and connection weights between nodes in two layers of a neural network, respectively: BP (first row) only conducts weights updates in one training epoch, while IL (second row) conducts inference until it converges (t = t c ) and updates weights (assuming T ≥ t c). Note that C1 is omitted in the figure for simplicity.