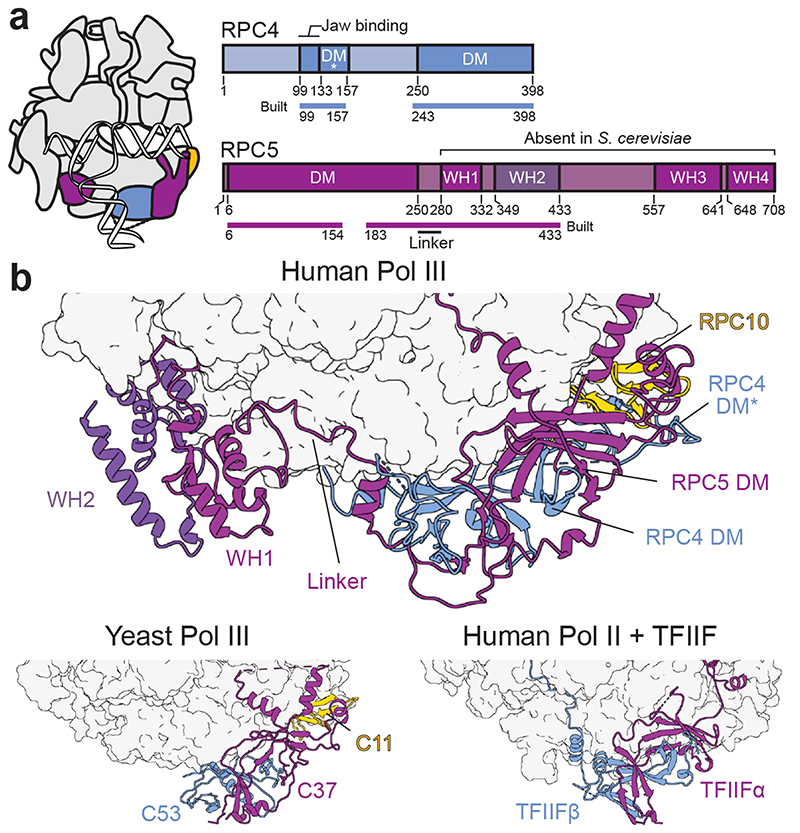
Fig. 3. Extended structure of human RPC4-RPC5.
a, Schematic domain organisation of subunits RPC4 and RPC5 in the elongating human Pol III complex. Coloured bars indicate modelled regions and are labelled as ‘built’. DM – dimerization module; DM* – RPC4 dimerization module extension; WH – winged-helix domain. Coloured bars indicate modelled regions and are labelled as ‘built’. b, Position of the RPC5 WH1 and WH2 domains, which are connected by a flexible linker to the DM of RPC4-RPC5 in the human Pol III EC (top). RPC4-RPC5 binds polymerase core via its DM domain in a similar fashion as C53-C37 in yeast Pol III (bottom left, PDB 5fj8) and TFIIF in the human Pol II PIC (bottom right, PDB 5iy6). Labelled subunits are shown as cartoons and polymerase cores as surfaces.