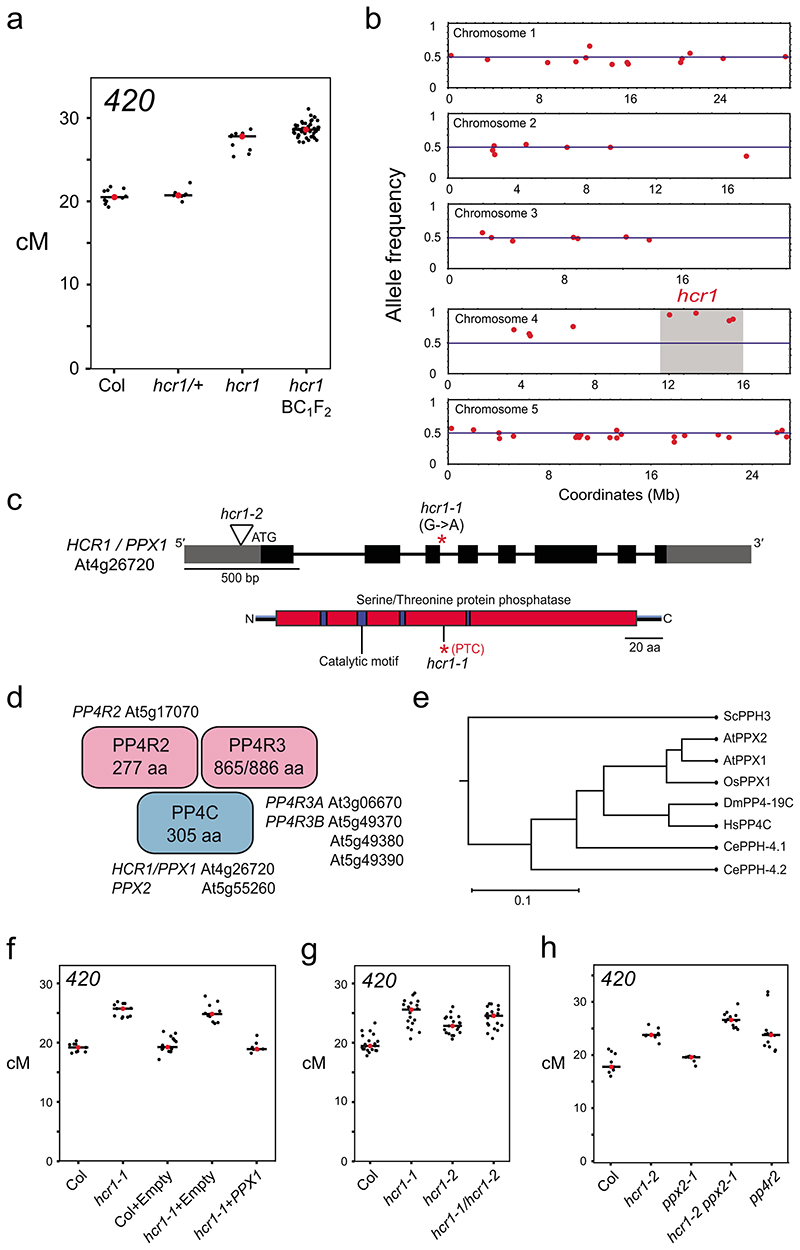
Figure 2. HIGH CROSSOVER RATE1 encodes PROTEIN PHOSPHATASE X1.
a, 420 crossover frequency (cM) in wild type, hcr1-1, hcr1-1/+ and high recombination hcr1-1 BC1F2 individuals used for DNA extraction and mapping-by-sequencing. Mean cM values are indicated by red dots and horizontal lines. b, Allele frequency of EMS mutations (red) identified by SHOREmap in high recombination hcr1-1 BC1F2 individuals. The blue horizontal line indicates 0.5 allele frequency. The hcr1-1 candidate region and mutations are highlighted on chromosome 4 with grey shading. c, HCR1/PPX1 gene with exons shown as boxes (black=CDS, grey=UTR) and the position of the hcr1-1 substitution. The hcr1-2 T-DNA insertion (triangle) is located in the gene 5’-UTR (triangle). A diagram of the HCR1/PPX1 protein is shown indicating the serine/threonine protein phosphatase domain (red), catalytic motifs (blue) and the position of the premature stop codon (*,PTC) caused by hcr1-1. d, A representation of the PP4 phosphatase complex with subunits (PP4C, PP4R2, PP4R3) shown and cognate Arabidopsis homologous genes. e, PPX/PP4C neighbor joining phylogenetic tree based on an alignment of amino acid sequences. The scale bar represents the number of changes per amino acid position. f, As for a, but showing 420 crossover frequency in hcr1-1 after transformation with PPX1 or empty vector constructs. g, As for a, but showing 420 crossover frequency in hcr1-1, hcr1-2 and hcr1-1/hcr1-2 F1 hybrids. h, 420 crossover frequency in the hcr1-2, ppx2 and pp4r2 mutants.