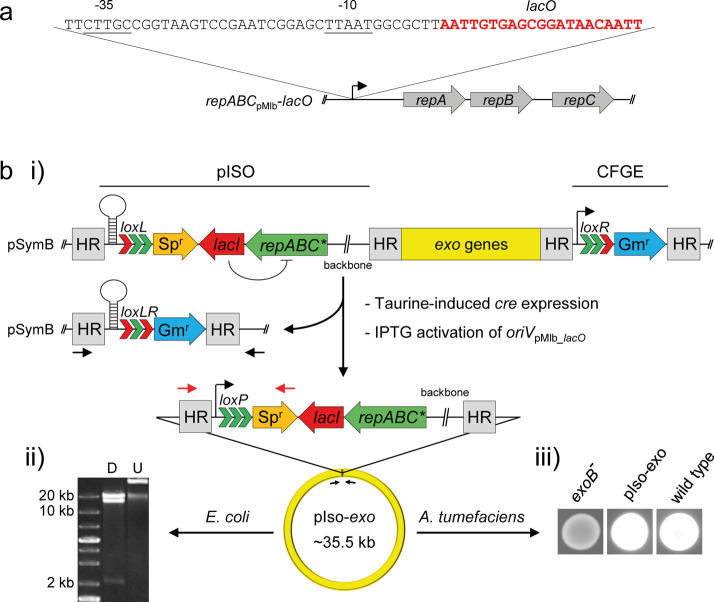
Figure 6.
repABC mediated in vivo cloning in S. meliloti (ABC cloning). (a) The promoter region of repABCpMLb was predicted according to the consensus motifs of S. meliloti σ70 promoters (−35 and −10 elements are underlined). A single lacO box (red letters) was integrated at the predicted transcription start site (+1). (b) ABC cloning of the exo gene cluster in S. meliloti SmCre. Three consecutive arrow heads indicate lox sites with native (green) or mutated arms (red). (i) A gentamicin resistance cassette carrying a right arm-mutated loxR site (Pmin2-loxR-aacC1) was integrated downstream of the gene cluster via cloning-free genome editing45 (CFGE). Subsequently, pISO bearing repABCpMlb-lacO (repABC*) was integrated via a ∼550 bp homologous region (HR) upstream of the gene cluster, resulting in S. meliloti SmCre_exo-IN. Taurine induction of Cre expression and simultaneous IPTG activation of oriVpMLb_lacO gave rise to SmCre_exo-OUT which carries the relocated ∼35.5 kb region (pIso-exo) comprising the entire exo gene cluster. Both the deletion site on pSymB and the fusion site on pIso-exo were PCR-amplified with primers 94 + Rev (black arrows) and 680 + 128 (red arrows), respectively, and sequencing of PCR products confirmed proper Cre-mediated recombination. (ii) pISO-exo was transferred to E. coli via triparental mating, resulting in E. coli/pIso-exo. Purified plasmid DNA was digested with NheI, resulting in fragments of 2.03 kb, 13.8 kb, and 19.6 kb fragments (D). Sequencing of the fusion site comprising loxP and aadA1 with primers 680 and 128 (red arrows) further confirmed successful cloning. U: Undigested plasmid DNA. (iii) Calcofluor fluorescence assay. pISO-exo was transferred to the exopolysaccharide-deficient A. tumefaciens C58 exoB mutant (exoB-) via triparental mating, giving rise to A. tumefaciens exoB/pIso-exo complemented for exopolysaccharide production (pIso-exo), and thus showing UV-induced fluorescence on Calcofluor-containing medium. Wild type: A. tumefaciens C58.