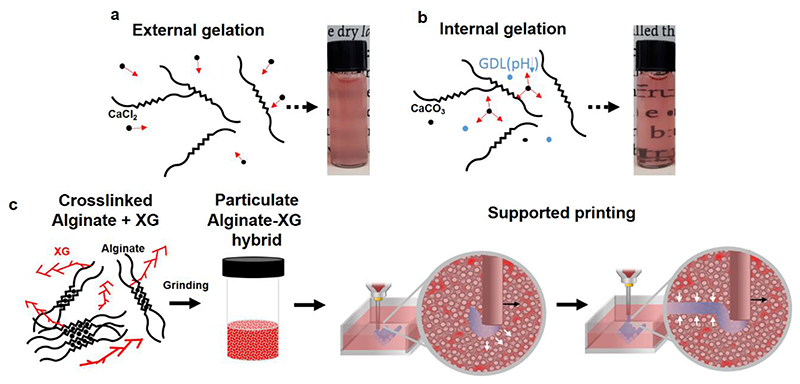
Figure 1. Concept schematic.
a. External and b. Internal gelation of alginate resulted in hydrogels that differ in their homogeneity and opacity. In the external gelation method, the alginate is non-homogenously crosslinked by diffusion of externally-introduced ions. In the internal gelation strategy, the crosslinking ion (such as Ca2+) is slowly liberated from a pre-mixed insoluble salt (such as CaCO3) upon acidification of the medium, resulting in homogenously crosslinked gels c. Preparation of the hybrid support medium for 3D printing. XG-supplemented alginate is slowly crosslinked by internal gelation and grinded to form a particulate hybrid medium. The latter is locally fluidized around the traversing needle and rapidly reorganizes to embrace and stabilize the printed strand.