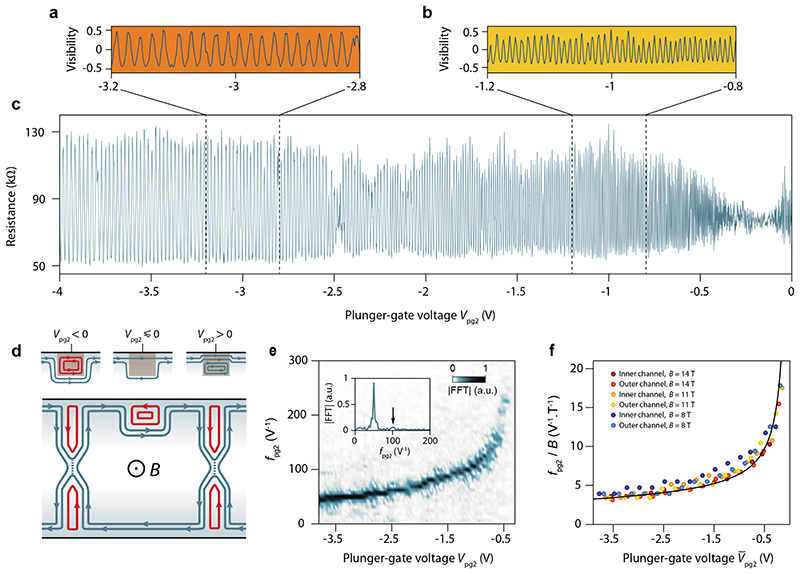
Fig. 2. Gate-tunable quantum interference.
a, b, c, Diagonal resistance oscillations as a function of plunger-gate voltage V pg2 measured on the small interferometer at 0.015 K and 14 T (with an ac bias voltage of 5μV). The back-gate voltage is set to V bg = 0.533 V corresponding to a filling factor νb = 1.5 in the bulk. The split-gate voltages on QPC2 and QPC3 are tuned to obtain partial transmission of the outer edge channel. The charge neutrality point below the plunger gate is at −0.3 V and corresponds to a suppression of the oscillation amplitude in c due to the divergence of the oscillation frequency shown in e. a and b show zooms on smaller V pg2 ranges of the resistance oscillations converted in visibility , where is the resistance average. d, Schematics of the QH-FP interferometer illustrating the edge channels configuration for the measurements in c. The black lines represent the physical edges of graphene. The blue (red) lines indicate electron(hole)-like edge channels and the arrows the direction of motion of charge carriers. At the QPC constriction, the dashed line indicates the tunneling of the interfering edge channel. Top sketches: Three configurations for the states around the plunger gate. Left, accumulation of localized hole states repelling the propagating electron edge channels. Middle, depletion of charge carrier density to a filling factor 1 below the gate, which repels the inner edge channel. Right, accumulation of localized electron states that push the propagating edge channels closer to the graphene edge. e, Fourier amplitude of the resistance oscillations in c as a function of V pg2 and the plunger-gate-voltage frequency ƒ pg2 obtained by computing the Fourier transform over a small Vpg2 window of 0.16 V sliding over the whole Vpg2 range. Inset : Fourier transform at V pg2 = –3.28 V showing a well-defined peak at ƒ pg2 = 50 V−1 and a faint peak at ƒ pg2 = 100 V−1 indicated by the black arrow. These peaks correspond to first order and second order (two turns in the FP loop) interference processes. f, Evolution of the main peak frequency ƒ pg2 rescaled by the magnetic field B as a function of , the plunger-gate voltage shifted with respect to the voltage that expels the interfering edge channel. The plot gathers a set of experiments performed with different interfering edge states and at different magnetic fields. The collapse of all data points into a single curve is fitted by an electrostatic simulation (see Supp. Section VIII) of the pn-junction displacement with plunger-gate voltage (black line).