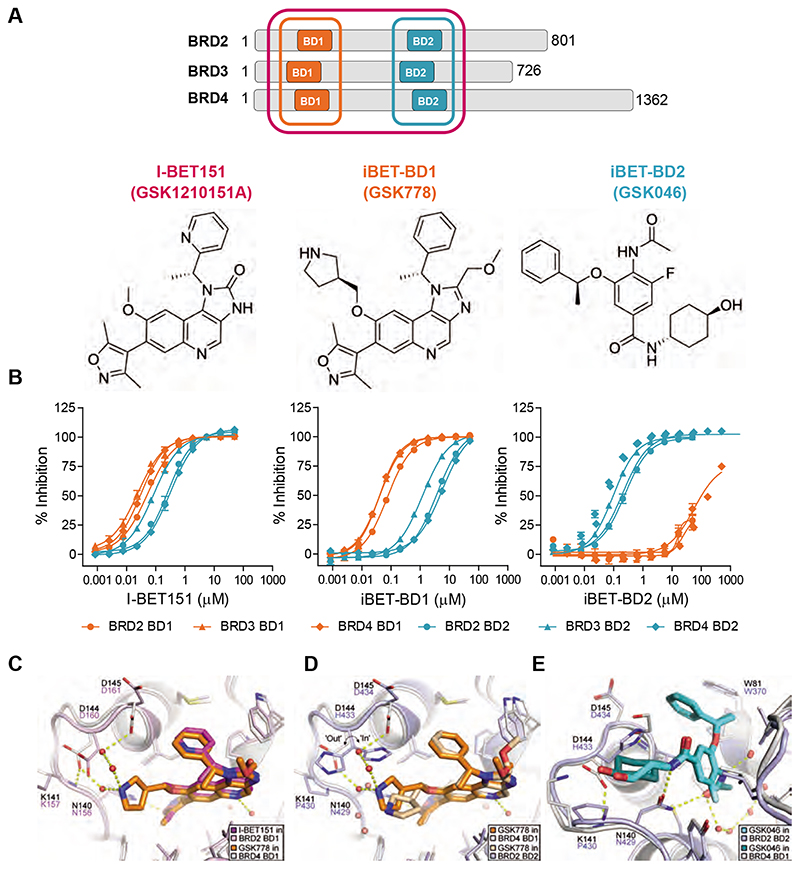
Fig. 1. Selectivity profile of I-BET151, iBET-BD1 (GSK778) and iBET-BD2 (GSK046).
(A) Schematic of the BET Bromodomain proteins and chemical structures. (B) Compound binding to the individual bromodomains of BD1 (orange) and BD2 (cyan) of BET tandem bromodomains in TR-FRET assays. (C) X-ray crystal structure of I-BET151 in BRD2 BD1 (magenta, PDB 4A1G)(19) superimposed on the structure of iBET-BD1 in BRD4 BD1 (orange, PDB 6SWN). (D) iBET-BD1 bound to BRD4 BD1 (dark orange/white, PDB 6SWN) and BRD2 BD2 (light orange/blue, PDB 6SWO) highlighting differences in the BC loop. (E) iBET-BD2 bound to BRD2 BD2 (light blue, PDB 6SWP) and BRD4 BD1 (cyan, PDB 6SWQ). In BRD2 BD2, the inhibitor’s benzyl and cyclohexane rings pack against Pro430 and His433, which adopts a single “in” conformation. In BRD4 BD1, iBET-BD2 makes no significant contacts with the corresponding Asp144 and Lys141 sidechains, and the space occupied by the His433 sidechain in BRD2 BD2 is filled by an ethane-1,2-diol molecule from the crystallisation buffer.