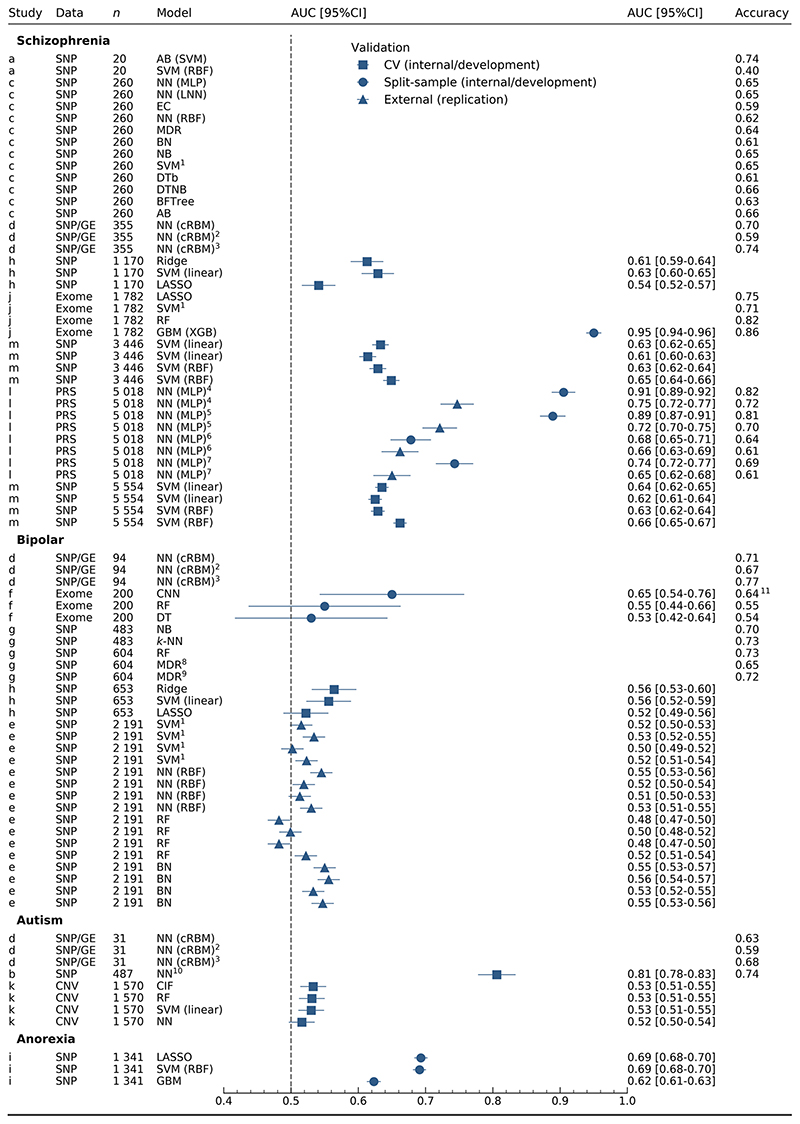
Figure 1. discrimination for all models.
n: number of cases in training set. Studies: a [35], b [40], c [34, 36], d [39], e [25], f [38], g [31], h [30], i [26], j [33], k [37], l [32], m [27]. 1SVM kernel not reported. 2Modified architecture with intermediate phenotypes in training set only. 3Modified architecture with intermediate phenotypes for training and test sets. 4,5,6,7Internal and external validation are shown for study l, where validations for the same model are denoted with the same number. 8Two-way MDR. 9Three-way MDR. 10Neural network embedding layer. 11Accuracy calculated from confusion matrix. AB: AdaBoost, BN: Bayesian networks, BFTree: best-first tree, CIF: conditional inference forest, cRBM: conditional restricted Boltzmann machine, CI: confidence interval, CNN: convolutional neural network, CNV: copy number variation, DTb: decision tables, DTNB: decision table naïve Bayes, DT: decision tree, EC: evolutionary computation, GE: gene expression, GBM: gradient boosting machine, k-NN: k-nearest neighbours, LASSO: least absolute shrinkage and selection operator, LNN: linear neural network, MDR: multifactor dimensionality reduction, MLP: multi-layer perceptron, NB: naïve Bayes, NN: neural network, PRS: polygenic risk scores, RBF: radial basis function, RF: random forests, SNP: single nucleotide polymorphisms, SVM: support vector machine, XGB: extreme gradient boosting.