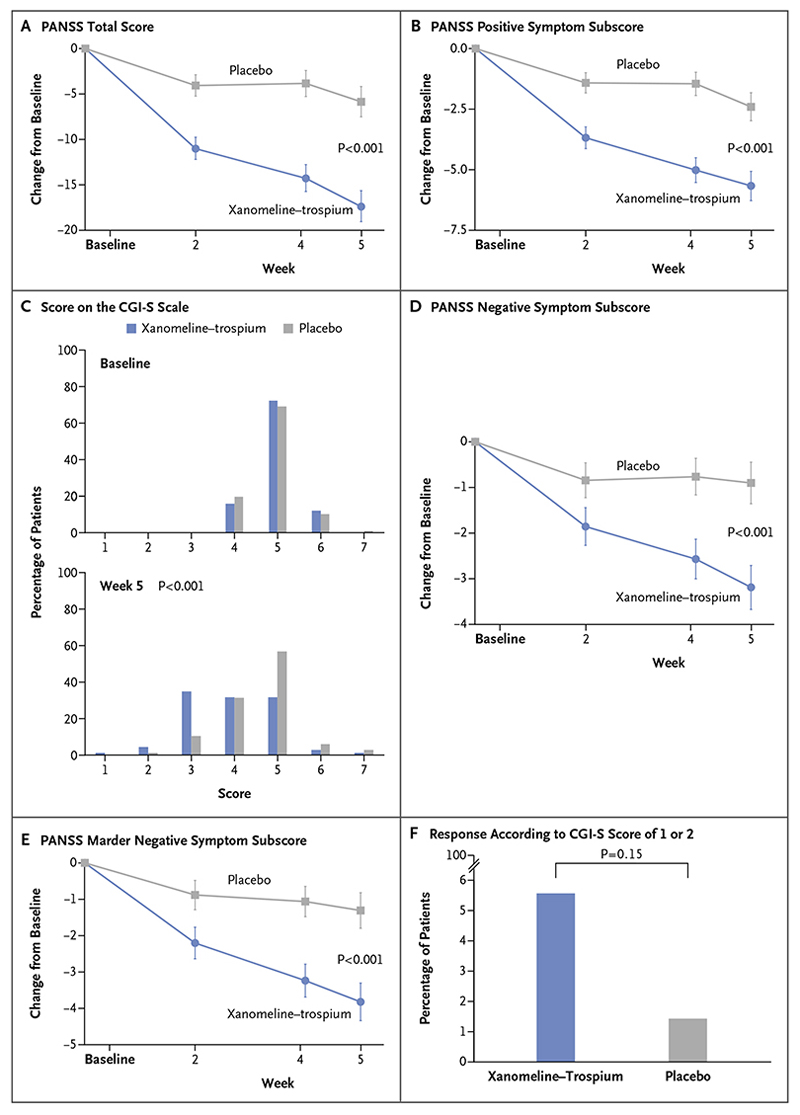
Figure 2 (facing page). Efficacy End Points.
The primary end point was the change from baseline to week 5 in the total score on the Positive and Negative Syndrome Scale (PANSS; range, 30 to 210, with higher scores indicating more severe symptoms of schizophrenia) (Panel A). The prespecified secondary efficacy end points are presented in the hierarchical order in which they were tested in the statistical analysis plan: the change in the PANSS positive symptom subscore (Panel B), the score on the Clinical Global Impression–Severity (CGI-S) scale (Panel C), the change in the PANSS negative symptom subscore (Panel D), the change in the PANSS Marder negative symptom subscore (Panel E), and the percentage of patients with a response according to a CGI-S score of 1 or 2 (Panel F). CGI-S scores range from 1 to 7, with higher scores indicating greater severity of illness. The PANSS positive symptom subscore, negative symptom subscore, and Marder negative symptom subscore each range from 7 to 49, with higher scores indicating greater severity of symptoms. All efficacy analyses were conducted in the modified intention-to-treat population. Changes in efficacy in continuous variable outcome measures (Panels A, B, D, and E) were evaluated with a mixed model for repeated measures, and differences in categorical variables were evaluated with nonparametric statistical tests (Mann–Whitney–Wilcoxon test, Panel C; Cochran–Mantel–Haenszel test, Panel F).