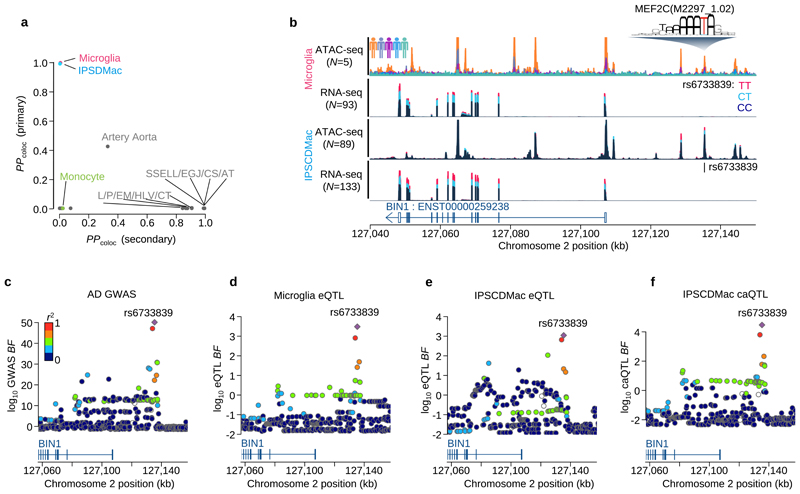
Figure 5. Fine-mapping of the BIN1 eQTL / Alzheimer’s disease association.
a. Posterior probability of colocalisation between Alzheimer’s disease27 and the three myeloid cells and GTEx eQTLs for the BIN1 gene. The y-axis is based on the AD GWAS primary signal of the BIN1 locus and the x-axis is based on the secondary signal at BIN1 found by the conditional analysis27. b. Sequencing coverage depth of ATAC-seq and RNA-seq stratified by individuals (top ATAC-seq panel) or the three genotype groups at BIN1 lead eQTL SNP (rs6733839C>T) (bottom three panels). The top two panels show data from the primary microglia (Materials and Methods) and the bottom two panels were obtained from iPS cell derived macrophage (Materials and Methods). The MEF2CA motif overlaps with the lead SNP and the alternative allele (T) increases predicted binding affinity. c. Regional Manhattan plot around the BIN1 gene. The y-axis shows the statistical significance of AD GWAS27 in log10 Bayes factor. d. Regional plot shows the statistical significance of microglia eQTL for BIN1 gene in log10 Bayes factor. e. Regional plot shows the statistical significance of IPSDMac eQTL for BIN1 gene in log10 Bayes factor. f. Regional plot shows the statistical significance of IPSDMac chromatin accessibility QTL (log10 Bayes factor) at the chromatin accessibility peak involving the putative causal variant rs6733839C>T. Tissue type annotation: Artery Tibial (AT), Esophagus Gastroesophageal Junction (EGJ), Colon Sigmoid (CS), Skin Sun Exposed Lower leg (SSELL), Heart Left Ventricle (HLV), Colon Transverse (CT), Esophagus Mucosa (EM), Pituitary (PI).