Fig. 5. Stoichiometry of the RNA degradosome.
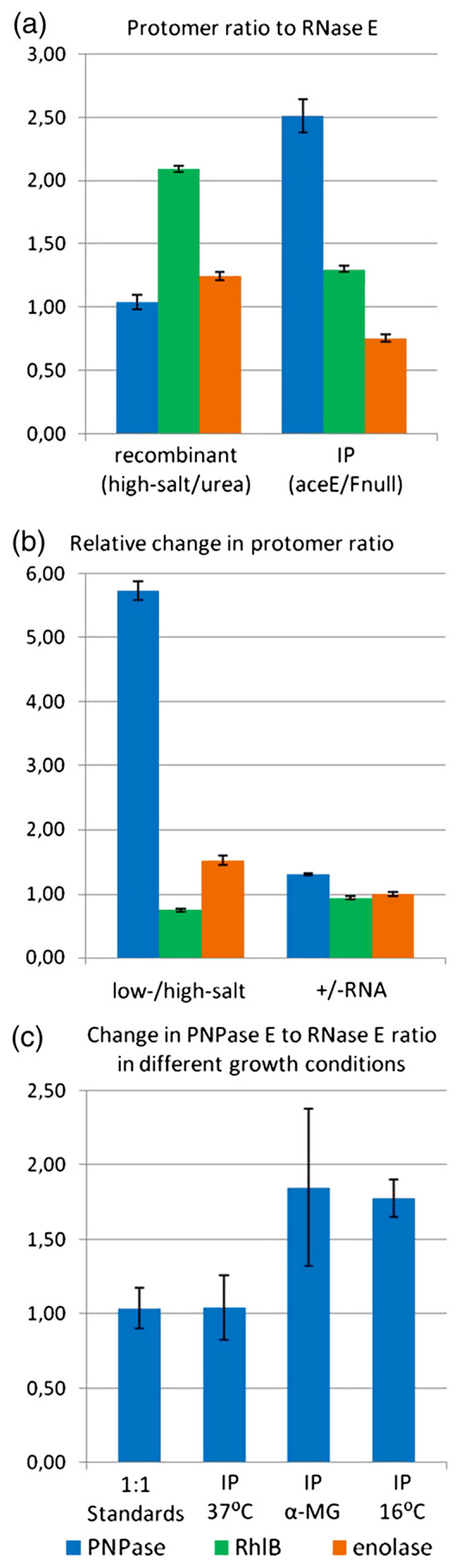
Band intensities obtained from gel densitometry were used to calculate internal ratios of PNPase, RhlB, and enolase to RNase E. (a) Internal ratios for high-salt/urea-treated recombinant degradosome and for FLAG-tagged degradosome purified from aceE/aceF-null cells to avoid crossreaction of the PDH with the FLAG antibody. The ratios were normalized using 1:1:1:1 standards prepared from purified recombinant components (see Supplementary Fig. S1). The RNase E level is set to unity. (b) An example of the change in internal ratios for components of the recombinant degradosome. Ratios for low-salt-extracted degradosome were divided by ratios of high-salt/urea-extracted degradosome. High-salt/urea degradosome was also purified with the addition of extra RNA, and the internal ratios were divided by ratios for the unmodified sample. Samples were taken from fractions at the same elution volume from size-exclusion chromatography. (c) PNPase/RNase E ratio determined for FLAG-tagged degradosomes purified from cells subjected to different growth conditions. αMG cells are cells grown in the presence of α-D-methylglucoside. Error bars are standard deviations that account for loading errors and background subtraction, and were estimated by running the samples in triplicate on SDS-PAGE.
