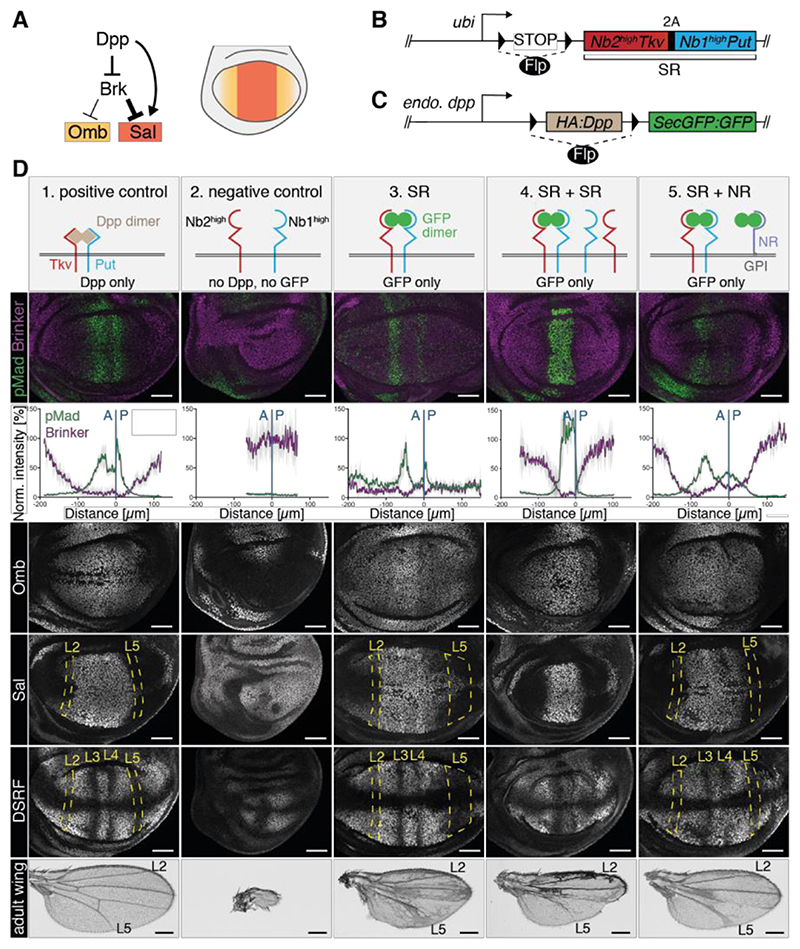
Fig. 4. Rescue of growth and patterning by GFP.
(A) Target genes of Dpp signaling in the pouch, which give rise to the wing. (B) Schematic representation of SR, the transgene for conditional expression of engineered receptors. (C) Dpp locus engineered to allow Flp-mediated replacement of an essential region by sequences encoding secreted GFP dimers. Throughout this study, rn-Gal4 and UAS-Flp were used to inactivate Dpp and/or trigger SR expression specifically in the pouch. (D) Phenotypes of wing imaginal discs and adult wings of various genotypes (columns). The positive control (column 1) shows imaginal discs and wings from a dpp-[>Dpp>SecGFP:GFP] homozygous larva. Flp is absent and Dpp is therefore expressed as in wild type discs. For the negative control (column 2), we used larvae homozygous for a different conditional allele (dpp-[>Dpp>]) (25) and carrying the SR transgene. Here, Flp expression inactivates Dpp in the pouch without triggering the GFP:GFP production, while at the same time activating expression of the engineered receptors. The resulting phenotypes recapitulated those of classical Dpp mutants (e.g. brk derepression and growth impairment). Abrogation of Dpp activity shows that the engineered receptors do not trigger signaling in the absence of GFP. If, in combination with the SR transgene, the dpp-[>Dpp>SecGFP:GFP] allele is used (column 3, SR), signaling activity (e.g. pMad immunoreactivity near the source) and growth are restored, albeit imperfectly. Note the occasional spots of pMad throughout the pouch, the expanded zone of brk repression, the fuzzy boundary of sal expression in the posterior compartment, and the disrupted vein pattern. Adding a second SR transgene (column 4, same genotype as in column 3 with one additional SR transgene, SR+SR) led to enhanced pMad at the source and a narrowing of the signaling gradient (relative to SR alone). Addition of non-signaling receptors (column 5, same genotype as in column 3 with addition of dally-NblowGPI, SR+NR) extended the signaling gradient (relative to SR alone). Note the absence of background pMad far from the source and the wild type-like expression of target genes. Note however that vein L4 was often disrupted and vein L5 was slightly broadened in the distal part. Scale bar wing discs: 50 μm. Scale bar adult wings: 0.25 mm.