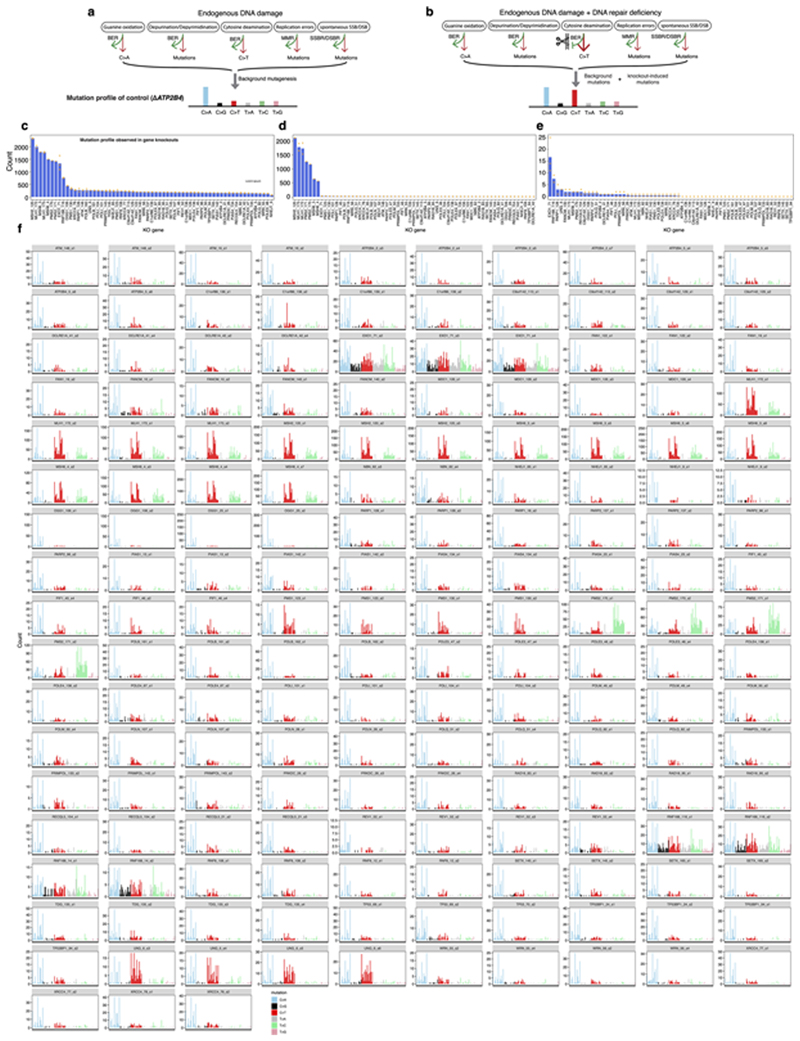
Extended Data Fig. 2. Detecting mutational consequences of knockouts in the absence of added external DNA damage.
(a)(b) Schematic illustration of potential components of background signature (a) and Possible mutational consequences of the DNA repair gene knockouts for proteins that are critical mitigators of mutagenesis (b). (c)-(e) Mutation burden of whole-genome-sequenced subclones of gene knockouts. (c) Substitution, (d) indel and (e) double substitution. Bars represent the mean. Individual data points are shown in orange dots. In all comparative analyses, all gene knockouts were cultured for 15 days and only daughter subclones that were fully clonal (i.e., clearly derived from a single cell) were included. N = 2~4, which is the number of clonal knockout subclones cultured under normoxic condition for 15 days (see Supplementary Table 2). (f) 96-channel substitution mutation profiles of 173 gene knockout subclones.