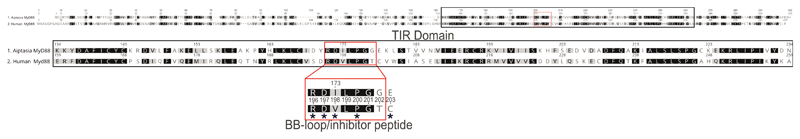
Extended Data Fig. 5. Amino acid sequence similarity between human and Aiptasia MyD88.
Human MyD88 homo-dimerizes to trigger a downstream signaling cascade leading to immune activation. It consists of three domains, the death domain (DD), the interdomain (ID) and the C-terminal TIR domain 97. The human TIR domain is key for homo-dimerization with other TIR domains from MyD88 or other TIR domain containing proteins. Three distinct regions contributing to homo-dimerization have been identified by crystallography, NMR and mammalian two-hybrid analysis 98. However, the so-called BB-loop within the TIR domain, a solvent-exposed stretch of 7 residues (RDLVPGT) is particularly critical for homodimerization in human MyD88. Accordingly, cell-permeable peptides mimicking the 7 residues of the BB-loop of human MyD88 interfere with homo-dimerization 99,55,100. The TIR domains (black box/upper alignment) of mammals and Aiptasia are well conserved (50% sequence identity). Moreover, the BB-loop (red box) is almost identical and key residues (*) are conserved. Identical amino acids have black background, similar aa have gray background and aa with white background are not similar according to blosume62 scoring.