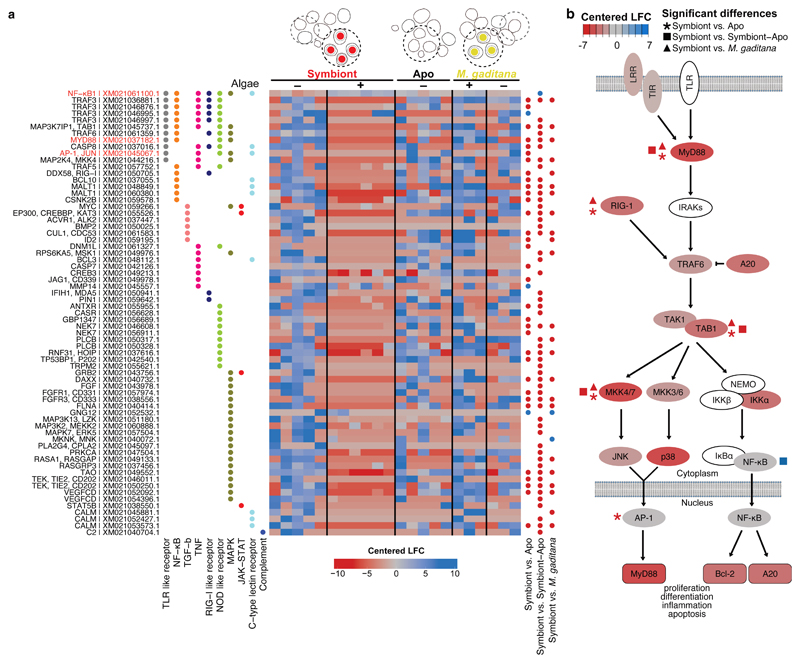
Fig. 4. Local suppression of host innate immunity is a prerequisite for symbiosis establishment.
a Several genes in immunity-related pathways were differentially downregulated in symbiont-containing cells but not in M. gaditana-containing cells or aposymbiotic cells from infected larvae (colors indicated centered log fold change according to Deseq2 with downregulation in red and upregulation in blue). The heatmap shows all differentially regulated genes symbiont vs Apo, symbiont vs symbiont-Apo, symbiont vs M. gaditana within the following KEGG pathways: C-type lectin receptor signaling pathway (ko04625), Complement and coagulation cascades (ko04610), JAK-STAT (ko04630), MAPK (ko04010), NF-κB (ko04064), NOD-like receptor (ko04621), RIG-I-like receptor (ko04622), TGFβ (ko04350), TNF (ko04668), and TLR-like receptor (ko04620). Significantly differentially expressed genes compared between populations of single cells are indicated with blue (upregulated) or red (downregulated) dots. Gene names in red indicate special interest as mentioned throughout the text. KEGG annotation was automated based on homology. b Simplified TLR pathway according to KEGG annotations (genes in white could not be identified in Aiptasia) representing gene expression in symbiotic cells (centered log fold change as in a). Statistically significant changes between symbiotic and aposymbiotic cells are indicated with asterisks, changes between symbiotic and aposymbiotic cells from symbiotic larvae are indicated with squares, and changes between symbiont- and M. gaditana-containing cells with triangles.