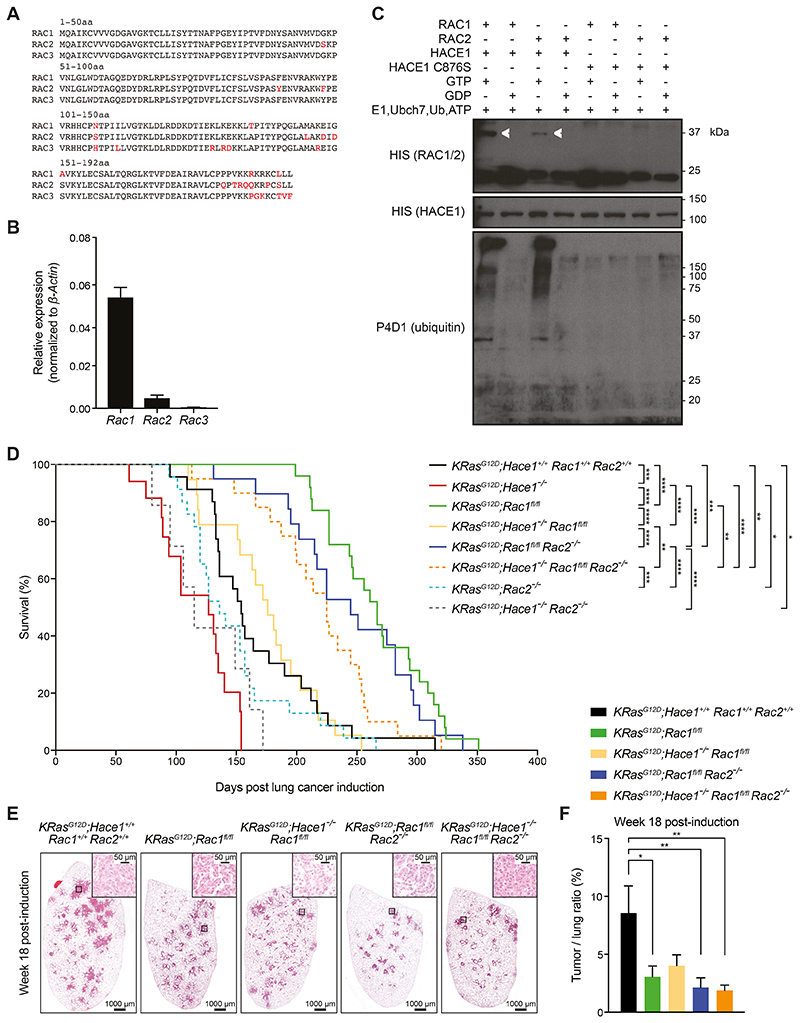
Figure 5. Simultaneous loss of Rac1 and Rac2 improves the survival of Hace1–/– mice.
(A) Amino acid (aa) sequence alignments of murine RAC1, RAC2, and RAC3. Amino acids highlighted in red indicate differences among the family members. The amino acid positions are indicted. (B) Relative mRNA expression of Rac1, Rac2 and Rac3 normalized to β-Actin expression in primary lung tumor cells, isolated from KRasG12D;Hace1+/+Rac1+/+Rac2+/+ mice (n=5) at week 7 post lung cancer induction, followed by RT-qPCR analysis. (C) In vitro ubiquitylation assay. Recombinant GST-HACE1 was incubated with GTP- or GDP-preloaded His-tagged RAC1 or RAC2 in the presence of E1, E2 (Ubch7), ubiquitin and ATP. As a control, catalytic dead HACE1C876S was used. Blots show RAC1 and RAC2 (detected via the His-tag), HACE1 and ubiquitin after 3 h incubation. Ubiquitylated RAC1 and RAC2 are indicated (white arrows). (D) Kaplan-Meier survival curves of KRasG12D;Hace1+/+Rac1+/+Rac2+/+ (n=23), KRasG12D;Hace1–/– (n=15), KRasG12D;Rac1fl/fl (n=25), KRasG12D;Hace1–/–Rac1fl/fl (n=19), KRasG12D;Rac2–/– (n=23) and KRasG12D;Hace1–/–Rac2–/– (n=7), KRasG12D;Rac1fl/flRac2–/– (n=19) and KRasG12D;Hace1–/–Rac1fl/flRac2–/– (n=20) mice. Mice were intratracheally instilled with Adeno-Cre virus on the indicated day 0. * P<0.05, ** P<0.01, *** P<0.001, **** P<0.0001 (log-rank test). (E) Representative H&E stained-lung sections and (F) tumor-to-lung ratios at week 18 post lung cancer induction for KRasG12D;Hace1+/+Rac1+/+Rac2+/+, KRasG12D;Rac1fl/fl, KRasG12D;Hace1–/–Rac1fl/fl, KRasG12D;Rac1fl/flRac2–/– and KRasG12D;Hace1–/–Rac1fl/flRac2–/– mice. Scale bars, 1 mm for 10x images and 50μm for 40x images of lung sections. * P<0.05, ** P<0.01 (One-way ANOVA, Tukey’s post-hoc test, n≥5 mice per cohort). Data in (B) and (F) are presented as mean values ± SEM.